Overview
The k-Truss algorithm identifies the largest cohesive subgraph, called a truss in the graph. It is widely used in fields such as social networks, biology, and transportation. By revealing communities or clusters of closely related nodes, it helps uncover the structure and connectivity of complex networks.
The concept of k-Truss was originally defined by J. Cohen in 2005:
- J. Cohen, Trusses: Cohesive Subgraphs for Social Network Analysis (2005)
Concepts
k-Truss
The truss is motivated by a natural observation of social cohesion: if two people are strongly tied, it is likely that they also share ties to others. A k-Truss is thus defined in this way: a tie between A and B is considered legitimate only if it is supported by at least k–2 other people who are each tied to both A and B. In other words, each edge in a k-truss connects two nodes that have at least k–2 common neighbors.
Formally,a k-truss is a maximal subgraph in which every edge is supported by at least k–2 triangles that include that edge.
In the graph below, the 3-Truss and 4-Truss are highlighted in red. The graph does not contain any truss with k equal to or greater than 5.
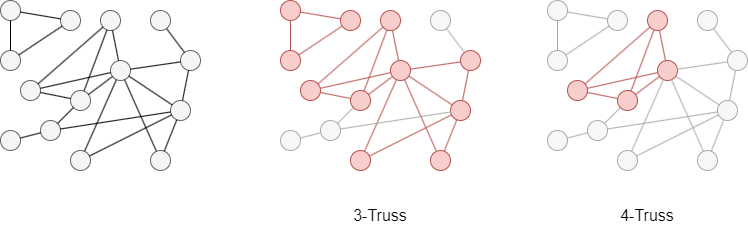
Ultipa's k-Truss algorithm identifies the maximal truss in each connected component.
Considerations
- At least 3 nodes are contained in a truss (when k≥3).
- In a complex graph with multiple edges between two nodes, triangles in a truss are counted based on edges. Refer to the Triangle Counting algorithm for additional context.
- The k-Truss algorithm treats all edges as undirected, ignoring their original direction.
Example Graph
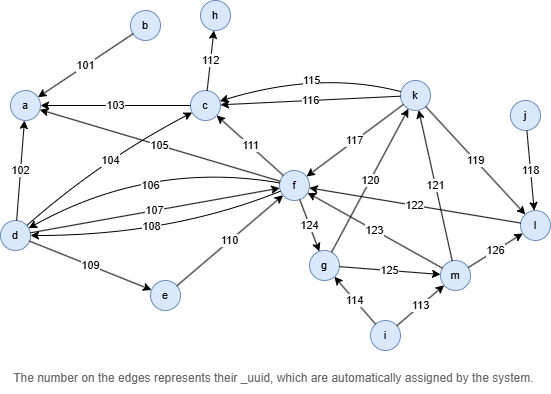
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
INSERT (a:default {_id: "a"}),
(b:default {_id: "b"}),
(c:default {_id: "c"}),
(d:default {_id: "d"}),
(e:default {_id: "e"}),
(f:default {_id: "f"}),
(g:default {_id: "g"}),
(h:default {_id: "h"}),
(i:default {_id: "i"}),
(j:default {_id: "j"}),
(k:default {_id: "k"}),
(l:default {_id: "l"}),
(m:default {_id: "m"}),
(b)-[:default]->(a),
(d)-[:default]->(a),
(c)-[:default]->(a),
(d)-[:default]->(c),
(f)-[:default]->(a),
(f)-[:default]->(d),
(d)-[:default]->(f),
(f)-[:default]->(d),
(d)-[:default]->(e),
(e)-[:default]->(f),
(f)-[:default]->(c),
(c)-[:default]->(h),
(i)-[:default]->(m),
(i)-[:default]->(g),
(k)-[:default]->(c),
(k)-[:default]->(c),
(k)-[:default]->(f),
(j)-[:default]->(l),
(k)-[:default]->(l),
(g)-[:default]->(k),
(m)-[:default]->(k),
(l)-[:default]->(f),
(m)-[:default]->(f),
(f)-[:default]->(g),
(g)-[:default]->(m),
(m)-[:default]->(l);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"a"}, {_id:"b"}, {_id:"c"}, {_id:"d"}, {_id:"e"}, {_id:"f"}, {_id:"g"}, {_id:"h"}, {_id:"i"}, {_id:"j"}, {_id:"k"}, {_id:"l"}, {_id:"m"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"b", _to:"a"}, {_from:"d", _to:"a"}, {_from:"c", _to:"a"}, {_from:"d", _to:"c"}, {_from:"f", _to:"a"}, {_from:"f", _to:"d"}, {_from:"d", _to:"f"}, {_from:"f", _to:"d"}, {_from:"d", _to:"e"}, {_from:"e", _to:"f"}, {_from:"f", _to:"c"}, {_from:"c", _to:"h"}, {_from:"i", _to:"m"}, {_from:"i", _to:"g"}, {_from:"k", _to:"c"}, {_from:"k", _to:"c"}, {_from:"k", _to:"f"}, {_from:"j", _to:"l"}, {_from:"k", _to:"l"}, {_from:"g", _to:"k"}, {_from:"m", _to:"k"}, {_from:"l", _to:"f"}, {_from:"m", _to:"f"}, {_from:"f", _to:"g"}, {_from:"g", _to:"m"}, {_from:"m", _to:"l"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: k_truss
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
k |
Integer | ≥1 | / | No | Each edge in the k-truss subgraph must be part of at least k-2 triangles. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. Edges can only be represented by _uuid; this option is only valid in File Writeback. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.k_truss.write("my_hdc_graph", {
k: 4,
return_id_uuid: "id"
}, {
file: {
filename: "4truss"
}
})
algo(k_truss).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
k: 4,
return_id_uuid: "id"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "4truss"
}
})
Result:
_id
e--[110]--f
k--[117]--f
k--[119]--l
m--[121]--k
m--[123]--f
m--[126]--l
c--[103]--a
g--[120]--k
g--[125]--m
d--[102]--a
d--[104]--c
d--[107]--f
d--[109]--e
f--[105]--a
f--[106]--d
f--[108]--d
f--[111]--c
f--[124]--g
l--[122]--f
Full Return
CALL algo.k_truss.run("my_hdc_graph", {
k: 5
}) YIELD truss
RETURN truss
exec{
algo(k_truss).params({
k: 5
}) as truss
return truss
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
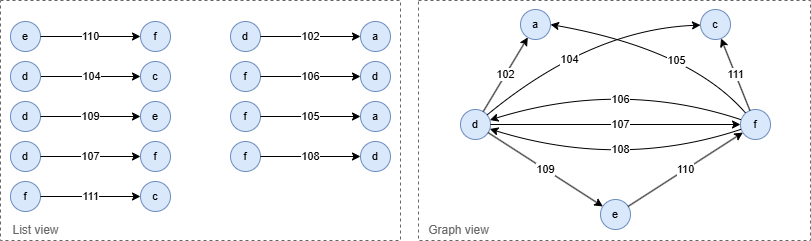
Stream Return
CALL algo.k_truss.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
k: 5
}) YIELD truss5
FOR node IN pnodes(truss5)
RETURN collect_list(node._id)
exec{
algo(k_truss).params({
k: 5
}).stream() as truss5
uncollect pnodes(truss5) as node
return collect(node._id)
} on my_hdc_graph
["d","a","d","c","d","f","d","e","f","a","f","d","f","d","f","c","e","f"]

