Aggregate Functions
Overview
An aggregate function performs a calculation on a set of values and returns a single scalar value.
NOTEVertical aggregation is supported which takes a set of values from different rows and aggregates into a single value. Horizontal aggregation which takes a set of values from a group list value and aggregates into a single value is not yet supported.
DISTINCT
All aggregate functions support the use of the set quantifier DISTINCT to deduplicate values before aggregation.
Null Values
Rows containing null values are ignored by all aggregate functions, except count(*).
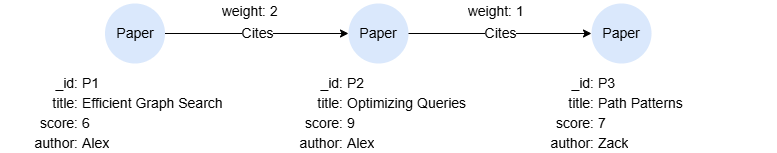
Example Graph
The following examples run against this graph:
avg()
Computes the average of a set of numeric values.
| Syntax | avg(<values>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Numeric | The target values | |
| Return Type | DOUBLE | ||
GQLMATCH (n) RETURN avg(n.score)
Result:
| avg(n.score) |
|---|
| 7.33333333333333 |
collect_list()
Collects a set of values into a list.
| Syntax | collect_list(<values>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Any | The target values | |
| Return Type | LIST | ||
GQLMATCH (n) RETURN collect_list(n.title)
Result:
| collect_list(n.title) |
|---|
| ["Optimizing Queries","Efficient Graph Search","Path Patterns"] |
count()
Returns the number of rows in the input.
| Syntax | count(<values>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Any | The target values | |
| Return Type | UINT | ||
GQLMATCH (n) RETURN count(n)
Result:
| count(n) |
|---|
| 3 |
count(*)
count(*) returns the number of rows in the intermediate result table.
Comparing the following two queries, the null values are only considered when using count(*):
GQLFOR item IN [1, "a", "2", "b3", null] RETURN count(item)
Result:
| count(item) |
|---|
| 4 |
GQLFOR item IN [1, "a", "2", "b3", null] RETURN count(*)
Result:
| count(*) |
|---|
| 5 |
count(DISTINCT)
You can include the set quantifier DISTINCT in count() to return the number of distinct rows in the input.
GQLFOR item IN [1, 1, "a", "2", "b3"] RETURN count(DISTINCT item)
Result:
| count(DISTINCT item) |
|---|
| 4 |
max()
Returns the maximum value in a set of values.
| Syntax | max(<values>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Any | The target values | |
| Return Type | Numeric | ||
GQLMATCH (n) RETURN max(n.score)
Result:
| max(n.score) |
|---|
| 9 |
GQLFOR item IN [1, "a", "2.1", "b3"] RETURN max(item)
Result:
| max(item) |
|---|
| 2 |
min()
Returns the minimum value in a set of values.
| Syntax | min(<values>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Any | The target values | |
| Return Type | Numeric | ||
GQLMATCH (n) RETURN min(n.score)
Result:
| min(n.score) |
|---|
| 6 |
GQLFOR item IN [3, "a", "0.2", "b2"] RETURN min(item)
Result:
| min(item) |
|---|
| 0 |
percentile_cont()
Computes the continuous percentile value over a set of numeric values.
| Syntax | percentile_cont(<values>, <percentile>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Numeric | The target values | |
<percentile> | Numeric | Number between 0.0 and 1.0 | |
| Return Type | DOUBLE | ||
percentile_cont() is computed using the following steps:
- Sort the values in ascending order.
- Compute the percentile position as
p = percentile × (n − 1) + 1, wherenis the number of non-null values. - Determine the percentile value using linear interpolation:
- If
pis an integer, the corresponding value at that position is the percentile value. - If
pis a decimal between two integersp1andp2(p1<p<p2), interpolate between the valuev1at positionp1and the valuev2at positionp2to compute the percentile value asv1 + (p - p1) × (v2 - v1).
- If
GQLFOR item IN [3, 9, 4, 7, 6] RETURN percentile_cont(item, 0.4)
Result:
| percentile_cont(item, 0.4) |
|---|
| 5.2 |
GQLFOR item IN [3, 9, 4, 7, 6] RETURN percentile_cont(item, 0.5)
Result:
| percentile_cont(item, 0.5) |
|---|
| 6 |
percentile_disc()
Computes the discrete percentile value over a set of numeric values.
| Syntax | percentile_disc(<values>, <percentile>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Numeric | The target values | |
<percentile> | Numeric | Number between 0.0 and 1.0 | |
| Return Type | DOUBLE | ||
percentile_disc() is computed using the following steps:
- Sort the values in ascending order.
- Compute the percentile position as
p = percentile × (n − 1) + 1, wherenis the number of non-null values. - Determine the percentile value:
- If
pis an integer, the value at that exact position is selected as the percentile value. - If
pis not an integer, it is rounded top', the value at the positionp'is selected as the percentile value.
- If
GQLFOR item IN [3, 9, 4, 7, 6] RETURN percentile_disc(item, 0.4)
Result:
| percentile_disc(item, 0.4) |
|---|
| 6 |
GQLFOR item IN [3, 9, 4, 7, 6] RETURN percentile_disc(item, 0.5)
Result:
| percentile_disc(item, 0.5) |
|---|
| 6 |
stddev_pop()
Computes the population standard deviation of a set of numeric values.
| Syntax | stddev_pop(<values>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Numeric | The target values | |
| Return Type | Numeric | ||
GQLMATCH (n) RETURN stddev_pop(n.score)
Result:
| stddev_pop(n.score) |
|---|
| 1.24721912892465 |
stddev_samp()
Computes the sample standard deviation of a set of numeric values.
| Syntax | stddev_samp(<values>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Numeric | The target values | |
| Return Type | DOUBLE | ||
GQLMATCH (n) RETURN stddev_samp(n.score)
Result:
| stddev_samp(n.score) |
|---|
| 1.52752523165195 |
sum()
Computes the sum of a set of numeric values.
| Syntax | sum(<values>) | ||
| Arguments | Name | Type | Description |
<values> | Numeric | The target values | |
| Return Type | DOUBLE | ||
GQLMATCH (n) RETURN sum(n.score)
Result:
| sum(n.score) |
|---|
| 22 |