Composite Query
Overview
A composite query combines the result sets of multiple linear queries using the following query conjunctions:
Query Conjunction | Description |
|---|---|
UNION | Returns distinct records from all result sets. |
UNION ALL | Returns all records from all result sets. |
EXCEPT | Returns distinct records in the 1st result set that do not appear in others. |
EXCEPT ALL | Returns all records in the 1st result set that do not appear in others. |
INTERSECT | Returns distinct records that appear in all result sets. |
INTERSECT ALL | Returns all records that appear in all result sets. |
OTHERWISE | Returns the first non-empty result set, in order of appearance. |
Details
UNION,EXCEPT, andINTERSECTperform deduplication on the final result set by default. They are equivalent toUNION DISTINCT,EXCEPT DISTINCT, andINTERSECT DISTINCT.- Different query conjunctions can be used within a composite query statement.
To combine the result sets of multiple linear queries, the RETURN statements in all linear queries include the same number of return items, in the same order and with the same names. Each return item with the same name must also have the same type.
Example Graph
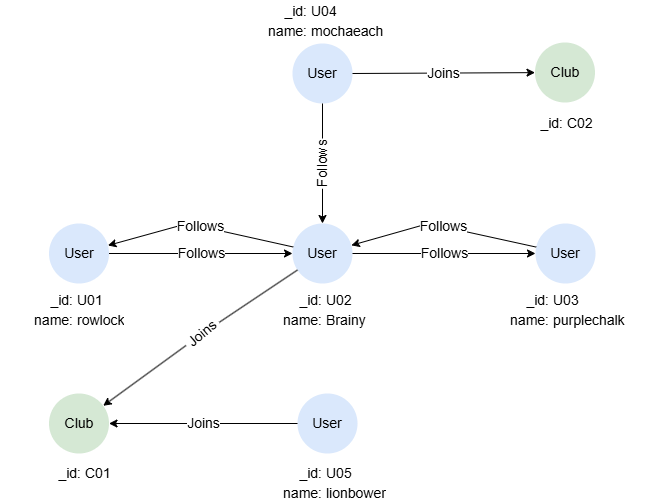
CREATE GRAPH myGraph { NODE User ({name string}), NODE Club (), EDGE Follows ()-[{}]->(), EDGE Joins ()-[{}]->() } PARTITION BY HASH(Crc32) SHARDS [1]
UNION
GQLMATCH (n:Club) RETURN n UNION MATCH (n) RETURN n
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| C02 | Sys-gen | Club | |
| C01 | Sys-gen | Club | |
| U05 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "lionbower"} |
| U04 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "mochaeach"} |
| U03 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "purplechalk"} |
| U02 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "Brainy"} |
| U01 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "rowlock"} |
UNION ALL
GQLMATCH (n:Club) RETURN n UNION ALL MATCH (n) RETURN n
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| C02 | Sys-gen | Club | |
| C01 | Sys-gen | Club | |
| U05 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "lionbower"} |
| U04 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "mochaeach"} |
| U03 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "purplechalk"} |
| U02 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "Brainy"} |
| U01 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "rowlock"} |
| C02 | Sys-gen | Club | |
| C01 | Sys-gen | Club |
EXCEPT
GQLMATCH ({_id: "U02"})-(n) RETURN n EXCEPT MATCH ({_id: "U05"})-(n) RETURN n
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| U04 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "mochaeach"} |
| U03 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "purplechalk"} |
| U01 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "rowlock"} |
EXCEPT ALL
GQLMATCH ({_id: "U02"})-(n) RETURN n EXCEPT ALL MATCH ({_id: "U05"})-(n) RETURN n
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| U01 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "rowlock"} |
| U03 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "purplechalk"} |
| U04 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "mochaeach"} |
| U03 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "purplechalk"} |
| U01 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "rowlock"} |
INTERSECT
GQLMATCH ({_id: "U01"})-(u:User) RETURN u INTERSECT MATCH ({_id: "U03"})-(u:User) RETURN u
Result: u
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| U02 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "Brainy"} |
INTERSECT ALL
GQLMATCH ({_id: "U01"})-(u:User) RETURN u INTERSECT ALL MATCH ({_id: "U03"})-(u:User) RETURN u
Result: u
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| U02 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "Brainy"} |
| U02 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "Brainy"} |
OTHERWISE
GQLMATCH ({_id: "U04"})<-[]-(u:User) RETURN u OTHERWISE MATCH ({_id: "U02"})<-[]-(u:User) RETURN u
Result: u
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| U01 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "rowlock"} |
| U03 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "purplechalk"} |
| U04 | Sys-gen | User | {name: "mochaeach"} |
In this example, the result set of the first linear query returns a null value due to the usage of OPTIONAL:
GQLOPTIONAL MATCH ({_id: "U04"})<-[]-(u:User) RETURN u OTHERWISE MATCH ({_id: "U02"})<-[]-(u:User) RETURN u
Result:
| u |
|---|
null |
Renaming Return Items
You may use the AS keyword to rename return items to ensure that the results of linear queries can be combined.
GQLMATCH ({_id: "C01"})<-(u) RETURN u.name, 1 AS Club UNION MATCH ({_id: "C02"})<-(u) RETURN u.name, 2 AS Club
Result:
| u.name | Club |
|---|---|
| Brainy | 1 |
| lionbower | 1 |
| mochaeach | 2 |
Using Different Query Conjunctions
GQLMATCH (n:Club) RETURN n._id OTHERWISE MATCH (n) RETURN n._id UNION ALL MATCH (n)-[]->(:Club) RETURN n._id
Result:
| n._id |
|---|
| C01 |
| C02 |
| U05 |
| U04 |
| U02 |
Deduplicating Multiple Return Items
When the RETURN statements contain multiple return items, DISTINCT removes duplicate records based on the combined values of all return items.
GQLMATCH (u1 {name: "rowlock"})-(u2:User) RETURN u1.name, u2.name UNION DISTINCT MATCH (u1 {name: "purplechalk"})-(u2:User) RETURN u1.name, u2.name
Result:
| u1.name | u2.name |
|---|---|
| rowlock | Brainy |
| purplechalk | Brainy |
You may compare the results returned by UNION ALL:
GQLMATCH (u1 {name: "rowlock"})-(u2:User) RETURN u1.name, u2.name UNION ALL MATCH (u1 {name: "purplechalk"})-(u2:User) RETURN u1.name, u2.name
Result:
| u1.name | u2.name |
|---|---|
| rowlock | Brainy |
| rowlock | Brainy |
| purplechalk | Brainy |
| purplechalk | Brainy |