Overview
The GROUP BY statement groups data based on a set of keys. When multiple keys are provided, grouping is applied sequentially from left to right: first by the first key, then by the second key within each group, and so on.
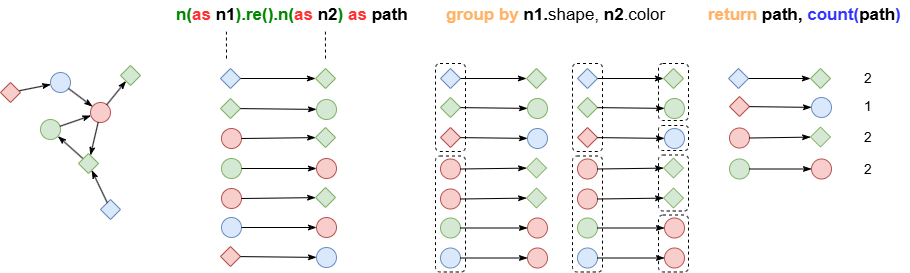
After grouping, each group retains only one record, discarding the others. However, when immediately used with aggregation functions like sum(), avg() and count(), these functions perform computations across all records within each group.
Syntax
GROUP BY <key1> as <alias1?>, <key2?> as <alias2?>, ...
WITH ...
Details
<key>: The grouping key which references an alias declared in previous statements.<alias?>: Declares alias for the grouping key; it is optional.- The
WITHstatement should be used immediately afterGROUP BYto extend the scope of necessary aliases and perform operations like aggregation within groups.
Example Graph
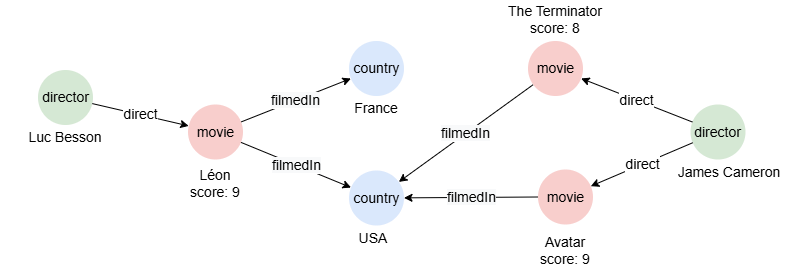
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().node_schema("country").node_schema("movie").node_schema("director").edge_schema("filmedIn").edge_schema("direct")
create().node_property(@*, "name").node_property(@movie, "score", float)
insert().into(@country).nodes([{_id:"C1", name:"France"}, {_id:"C2", name:"USA"}])
insert().into(@movie).nodes([{_id:"M1", name:"Léon", score: 9}, {_id:"M2", name:"The Terminator", score: 8}, {_id:"M3", name:"Avatar", score: 9}])
insert().into(@director).nodes([{_id:"D1", name:"Luc Besson"}, {_id:"D2", name:"James Cameron"}])
insert().into(@filmedIn).edges([{_from:"M1", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"M1", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"M2", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"M3", _to:"C2"}])
insert().into(@direct).edges([{_from: "D1", _to: "M1"}, {_from: "D2", _to: "M2"}, {_from: "D2", _to: "M3"}])
Grouping
To find movies and group them by their score:
find().nodes({@movie}) as m
group by m.score
with m
return table(m.name, m.score)
Only one record is kept for each score value after grouping:
| m.name | m.score |
|---|---|
| The Terminator | 8.000000 |
| Avatar | 8.000000 |
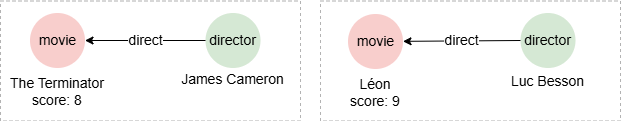
To find paths linking @movie and @director, then group them by the director:
n({@movie}).e().n({@director} as d) as p
group by d
with d, p
return p{*}
Only one path is kept for each director after grouping:
Result: p
Grouping with Aggregation
To find paths linking @movie and @director, and count the number of movies produced by each director:
n({@movie}).e().n({@director} as d)
group by d
with d, count(d) as cnt
return table(d.name, cnt)
The aggregation count() operates on all records in each group:
| d.name | cnt |
|---|---|
| James Cameron | 2 |
| Luc Besson | 1 |
Multi-level Grouping
To find paths linking @country, @movie and @director, then group them by the country and director, and count the number of movies in each group:
n({@country} as c).e().n({@movie}).e().n({@director} as d) as p
group by c, d
with c, d, count(p) as cnt
return table(c.name, d.name, cnt)
Result:
| c.name | d.name | cnt |
|---|---|---|
| USA | James Cameron | 2 |
| USA | Luc Besson | 1 |
| France | Luc Besson | 1 |

