Overview
The Induced Subgraph algorithm computes the subgraph formed by a given set of nodes and the edges connecting them within the original graph. This enables focused analysis of local structure and interactions, providing insights into the immediate connections among the selected nodes.
Concepts
Induced Subgraph
An induced subgraph includes only the nodes from the given set and the edges that connect those nodes.
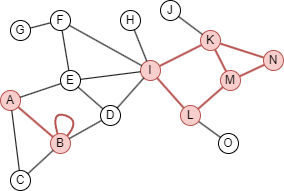
As this example shows, when specifying node set S = {A, B, I, K, L, M, N}, the induced subgraph is the graph whose node set is S and whose edge set contains all edges that have both endpoints in S.
Ultipa's Induced Subgraph algorithm returns all 1-step paths in the induced subgraph.
Considerations
- The Induced Subgraph algorithm treats all edges as undirected, ignoring their original direction.
Example Graph
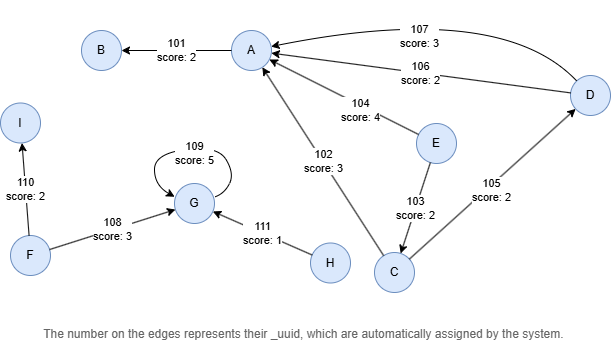
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
ALTER EDGE default ADD PROPERTY {
score int32
};
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A"}),
(B:default {_id: "B"}),
(C:default {_id: "C"}),
(D:default {_id: "D"}),
(E:default {_id: "E"}),
(F:default {_id: "F"}),
(G:default {_id: "G"}),
(H:default {_id: "H"}),
(I:default {_id: "I"}),
(A)-[:default {score: 2}]->(B),
(C)-[:default {score: 3}]->(A),
(E)-[:default {score: 2}]->(C),
(E)-[:default {score: 4}]->(A),
(C)-[:default {score: 2}]->(D),
(D)-[:default {score: 2}]->(A),
(D)-[:default {score: 3}]->(A),
(F)-[:default {score: 3}]->(G),
(G)-[:default {score: 5}]->(G),
(F)-[:default {score: 2}]->(I),
(H)-[:default {score: 1}]->(G);
create().edge_property(@default, "score", int32);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}, {_id:"G"}, {_id:"H"}, {_id:"I"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"B", score:2}, {_from:"C", _to:"A", score:3}, {_from:"E", _to:"C", score:2}, {_from:"E", _to:"A", score:4}, {_from:"C", _to:"D", score:2}, {_from:"D", _to:"A", score:2}, {_from:"D", _to:"A", score:3}, {_from:"F", _to:"G", score:3}, {_from:"G", _to:"G", score:5}, {_from:"F", _to:"I", score:2}, {_from:"H", _to:"G", score:1}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: subgraph
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ids |
[]_id |
/ | / | No | Specifies nodes for computation by their _id. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
uuids |
[]_uuid |
/ | / | No | Specifies nodes for computation by their _uuid. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. Edges can only be represented by _uuid. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.subgraph.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['A','C','D','G']
}, {
file: {
filename: "paths"
}
})
algo(subgraph).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['A','C','D','G']
}).write({
file: {
filename: "paths"
}
})
Result:
_id
C--[102]--A
D--[107]--A
D--[106]--A
C--[105]--D
G--[109]--G
Full Return
CALL algo.subgraph.run("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['A','C','D','G']
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(subgraph).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['A','C','D','G']
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
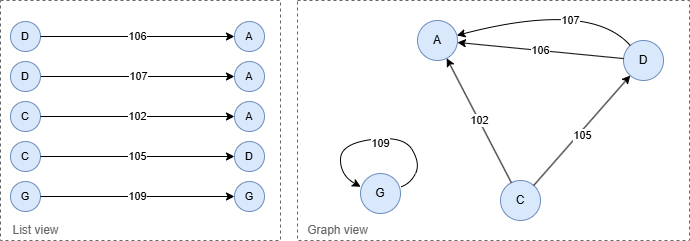
Stream Return
CALL algo.subgraph.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['F','G']
}) YIELD p
FOR e1 IN pedges(p)
MATCH ()-[e2 WHERE e2._uuid = e1._uuid]->()
RETURN max(e2.score)
exec{
algo(subgraph).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['F','G']
}).stream() as p
uncollect pedges(p) as e1
find().edges({_uuid == e1._uuid}) as e2
return max(e2.score)
} on my_hdc_graph
Result: 5

