Overview
The Degree Centrality algorithm is used to find important nodes in the network, it measures the number of incoming and/or outgoing edges incident to the node, or the sum of weights of those edges. Degree is the simplest and most efficient graph algorithm since it only considers the 1-hop neighborhood of nodes. Degree plays a vital role in scientific computing, feature extraction, supernode recognition and other fields.
Concepts
In-Degree and Out-Degree
The number of incoming edges a node has is called its in-degree; accordingly, the number of outgoing edges is called out-degree. If ignores edge direction, it is degree.
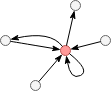
In this graph, the red node has in-degree of 4 and out-degree of 3, and its degree is 7. A directed self-loop is regarded as both an incoming and an outgoing edge.
Weighted Degree
In many applications, each edge of a graph has an associated numeric value, called weight. In weighted graph, weighted degree of a node is the sum of weights of all its neighbor edges. Unweighted degree is equivalent to when all edge weights are 1.
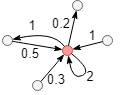
In this weighted graph, the red node has weighted in-degree of 0.5 + 0.3 + 2 + 1 = 3.8 and weighted out-degree of 1 + 0.2 + 2 = 3.2, and its weighted degree is 3.2 + 3.8 = 7.
Considerations
- The degree of an isolated node depends only on its self-loop. If it has no self-loop, degree is 0.
- Every self-loop is counted as two edges attaching to its node. Directed self-loop is viewed as an incoming edge and an outgoing edge.
Example Graph
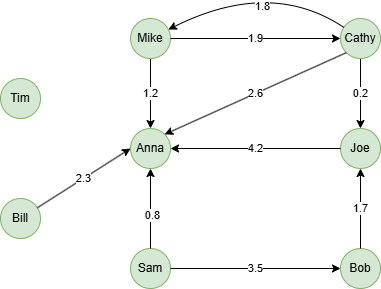
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD NODE {
user ()
};
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD EDGE {
follow ()-[{score float}]->()
};
INSERT (Mike:user {_id: "Mike"}),
(Cathy:user {_id: "Cathy"}),
(Anna:user {_id: "Anna"}),
(Joe:user {_id: "Joe"}),
(Sam:user {_id: "Sam"}),
(Bob:user {_id: "Bob"}),
(Bill:user {_id: "Bill"}),
(Tim:user {_id: "Tim"}),
(Mike)-[:follow {score: 1.9}]->(Cathy),
(Cathy)-[:follow {score: 1.8}]->(Mike),
(Mike)-[:follow {score: 1.2}]->(Anna),
(Cathy)-[:follow {score: 2.6}]->(Anna),
(Cathy)-[:follow {score: 0.2}]->(Joe),
(Joe)-[:follow {score: 4.2}]->(Anna),
(Bob)-[:follow {score: 1.7}]->(Joe),
(Sam)-[:follow {score: 3.5}]->(Bob),
(Sam)-[:follow {score: 0.8}]->(Anna),
(Bill)-[:follow {score: 2.3}]->(Anna);
create().node_schema("user").edge_schema("follow");
create().edge_property(@follow, "score", float);
insert().into(@user).nodes([{_id:"Mike"},{_id:"Cathy"},{_id:"Anna"},{_id:"Joe"},{_id:"Sam"},{_id:"Bob"},{_id:"Bill"},{_id:"Tim"}]);
insert().into(@follow).edges([{_from:"Mike", _to:"Cathy", score:1.9}, {_from:"Cathy", _to:"Mike", score:1.8}, {_from:"Mike", _to:"Anna", score:1.2},{_from:"Cathy", _to:"Anna", score:2.6},{_from:"Cathy", _to:"Joe", score:0.2},{_from:"Joe", _to:"Anna", score:4.2},{_from:"Bob", _to:"Joe", score:1.7},{_from:"Sam", _to:"Bob", score:3.5},{_from:"Sam", _to:"Anna", score:0.8},{_from:"Bill", _to:"Anna", score:2.3}]);
Running on HDC Graphs
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: degree
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ids |
[]_id |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies nodes for computation by their _id. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
uuids |
[]_uuid |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies nodes for computation by their _uuid. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
edge_schema_property |
[]"<@schema.?><property>" |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies numeric edge properties used to compute weighted degrees by summing their values. Only properties of numeric type are considered, and edges without these properties are ignored. |
direction |
String | in, out |
/ | Yes | Specifies in for in-degrees, out for out-degrees. If unset, general degree is computed. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both values in the results to represent nodes. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
order |
String | asc, desc |
/ | Yes | Sorts the results by degree_centrality. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.degree.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
order: "desc"
}, {
file: {
filename: "degree"
}
})
algo(degree).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
order: "desc"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "degree"
}
})
Result:
_id,degree_centrality
Anna,5
Cathy,4
Joe,3
Mike,3
Bob,2
Sam,2
Bill,1
Tim,0
DB Writeback
Writes the degree_centrality values from the results to the specified node property. The property type is double.
CALL algo.degree.write("my_hdc_graph", {
edge_schema_property: 'score'
}, {
db: {
property: "degree"
}
})
algo(degree).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
edge_schema_property: 'score'
}).write({
db:{
property: 'degree'
}
})
Full Return
CALL algo.degree.run("my_hdc_graph", {
edge_schema_property: 'score',
return_id_uuid: "id",
order: 'desc'
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(degree).params({
edge_schema_property: 'score',
return_id_uuid: "id",
order: 'desc'
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id | degree_centrality |
|---|---|
| Anna | 11.1 |
| Cathy | 6.5 |
| Joe | 6.1 |
| Bob | 5.2 |
| Mike | 4.9 |
| Sam | 4.3 |
| Bill | 2.3 |
| Tim | 0 |
Stream Return
To find neighbors of the node with the highest out-degree:
CALL algo.degree.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
direction: "out",
order: "desc",
limit: 1
}) YIELD outTop1
MATCH (src WHERE src._uuid = outTop1._uuid)-(neigh)
RETURN DISTINCT neigh._id
exec{
algo(degree).params({
direction: "out",
order: "desc",
limit: 1
}).stream() as outTop1
khop().src({_uuid == outTop1._uuid}).depth(1) as neigh
return neigh._id
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| neigh._id |
|---|
| Anna |
| Joe |
| Mike |
Running on Distributed Projections
Creating Distributed Projection
To project the entire graph to its shard servers as myProj:
CREATE PROJECTION myProj OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true
}
create().projection("myProj", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true
})
Parameters
Algorithm name: degree
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
edge_schema_property |
"<@schema.?><property>" |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies numeric edge properties used to compute weighted degrees. Only properties of numeric type are considered, and edges without these properties are ignored. |
direction |
String | in, out |
/ | Yes | Specifies in for in-degrees, out for out-degrees. If unset, general degree is computed. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
order |
String | asc, desc |
/ | Yes | Sorts the results by degree_centrality. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.degree.write("myProj", {
order: "desc"
}, {
file: {
filename: "degree"
}
})
algo(degree).params({
projection: "myProj",
order: "desc"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "degree"
}
})
Result:
_id,degree_centrality
Anna,5
Cathy,4
Joe,3
Mike,3
Bob,2
Sam,2
Bill,1
Tim,0
DB Writeback
Writes the degree_centrality values from the results to the specified node property. The property type is double.
CALL algo.degree.write("myProj", {
edge_schema_property: 'score'
}, {
db: {
property: "degree"
}
})
algo(degree).params({
projection: "myProj",
edge_schema_property: 'score'
}).write({
db:{
property: 'degree'
}
})

