Overview
The WHERE statement filters records contained in data, retaining those that meet the specified conditions and discarding those that do not.
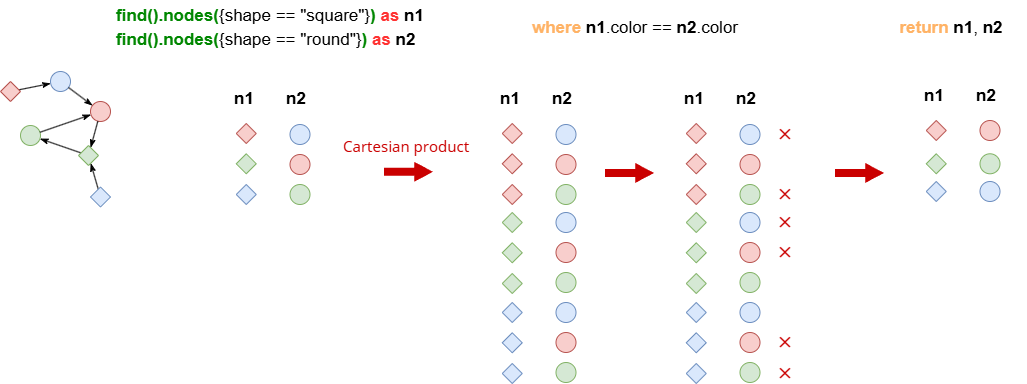
Syntax
WHERE <conditions>
Details
<condition>: The conditions used to filter records. You may use logical operators like&&and||to combine multiple conditions if necessary. Only those that evaluate to TRUE will be retained.- Note that a Cartesian product will be performed between if heterologous aliases are referenced in
<condition>.
Example Graph
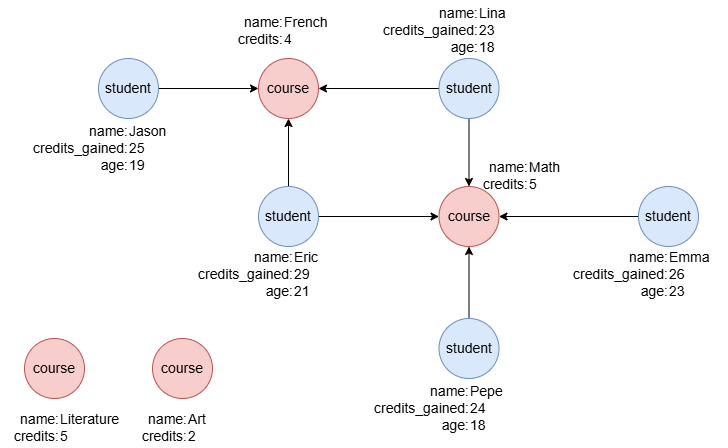
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().node_schema("student").node_schema("course").edge_schema("takes")
create().node_property(@*, "name").node_property(@student, "credits_gained", int32).node_property(@course, "credits", int32).node_property(@student, "age", int32)
insert().into(@student).nodes([{_id:"S1", name:"Jason", credits_gained:25, age:19}, {_id:"S2", name:"Lina", credits_gained:23, age:18}, {_id:"S3", name:"Eric", credits_gained:29, age:21}, {_id:"S4", name:"Emma", credits_gained:26, age:23}, {_id:"S5", name:"Pepe", credits_gained:24, age:18}])
insert().into(@course).nodes([{_id:"C1", name:"French", credits:4}, {_id:"C2", name:"Math", credits:5}, {_id:"C3", name:"Literature", credits:5}, {_id:"C4", name:"Art", credits:2}])
insert().into(@takes).edges([{_from:"S1", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"S2", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"S3", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"S2", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"S3", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"S4", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"S5", _to:"C2"}])
Without Cartesian Product
find().nodes({@student}) as stu
where stu.credits_gained > 25
return stu.name
Result:
| stu.name |
|---|
| Eric |
| Emma |
find().nodes({@student}) as stu
where stu.credits_gained > 25 && stu.age > 21
return stu.name
Result:
| stu.name |
|---|
| Emma |
With Cartesian Product
find().nodes({@student}) as stu
find().nodes({@course.name in ["Literature", "Art"]}) as newCrs
where stu.credits_gained + newCrs.credits > 30
return table(stu.name, newCrs.name, stu.credits_gained + newCrs.credits)
Result:
| stu.name | newCrs.name | ADD(stu.credits_gained,newCrs.credits) |
|---|---|---|
| Eric | Art | 31 |
| Eric | Literature | 34 |
| Emma | Literature | 31 |

