Overview
The spread().src().depth() statement performs a breadth first search (BFS), spreading outward from each traversal source. It retrieves one-step paths from the traversal source, layer by layer, expanding to its neighbors in order of increasing depth.
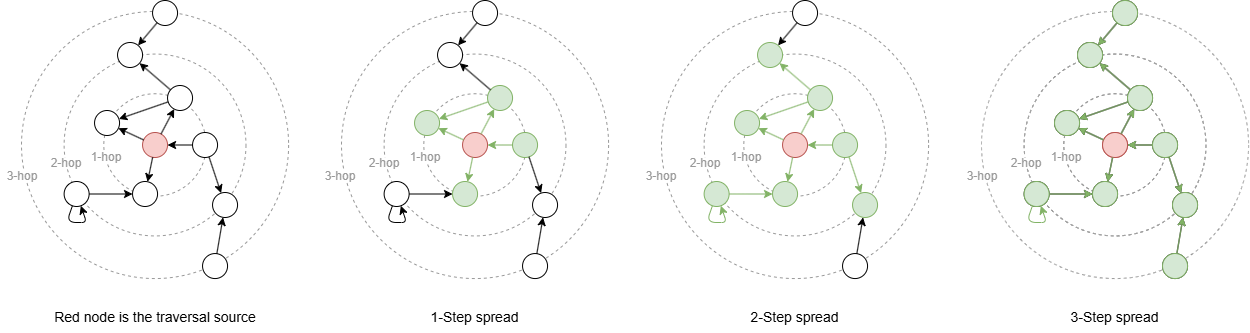
This illustrates the process of spreading from a traversal source (represented as the red node). At each k-step:
- It identifies one-step paths between the
k-1hop neighbors (which correspond to the traversal source atk = 1) and thekhop neighbors of the traversal source. - Simultaneously, it discovers one-step paths between the
khop neighbors themselves, including self-loops on thekhop neighbors. - Specifically, self-loops on the traversal source are identified at step 1.
Syntax
spread().src(<filter?>).depth(<steps>)
- Statement alias: Type
PATH - Methods:
Method |
Param |
Description | Optional |
Alias Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
src() |
<filter?> |
The filtering condition enclosed in {}, or an alias to specify the set of nodes as traversal sources. Leaving it blank will target all nodes. |
No | NODE |
depth() |
<steps> |
The maximum number of steps (≥1) to spread. | No | N/A |
node_filter() |
<filter?> |
The filtering condition enclosed in {} for all nodes other than the traversal sources in the paths. Leaving it blank applies no restriction. |
Yes | N/A |
edge_filter() |
<filter?> |
The filtering condition enclosed in {} for edges in the paths. Leaving it blank applies no restriction. |
Yes | N/A |
direction() |
<leftRight> |
Specifies the direction of edges to traverse when spreading outward, which can be left or right. |
Yes | N/A |
limit() |
<N> |
Limits the number of paths (N≥-1) returned for each traversal source; -1 includes all paths. |
Yes | N/A |
Example Graph
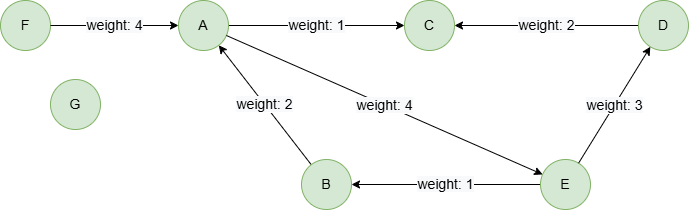
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().edge_property(@default, "weight", int32)
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}, {_id:"G"}])
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"C", weight:1}, {_from:"E", _to:"B", weight:1}, {_from:"A", _to:"E", weight:4}, {_from:"D", _to:"C", weight:2}, {_from:"E", _to:"D", weight:3}, {_from:"B", _to:"A", weight:2}, {_from:"F", _to:"A", weight:4}])
Spreading From Nodes
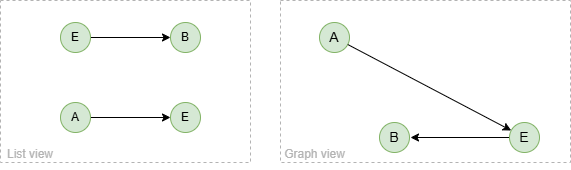
To spread from node B with 1 step:
spread().src({_id == "B"}).depth(1) as p
return p
Result: p
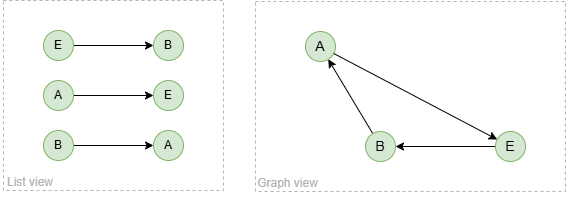
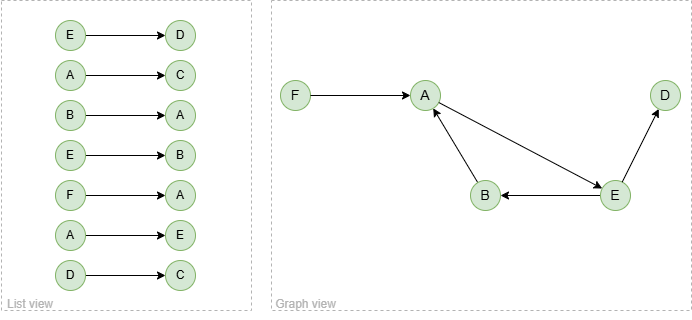
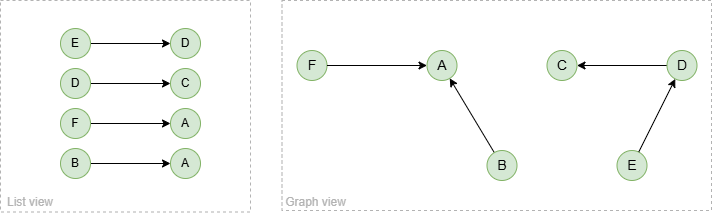
To spread from node B with 2 steps:
spread().src({_id == "B"}).depth(2) as p
return p
Result: p
Filtering Neighbor Nodes
To spread from node D with 2 steps while excluding node E:
spread().src({_id == "D"}).depth(2).node_filter({_id != "E"}) as p
return p
Result: p
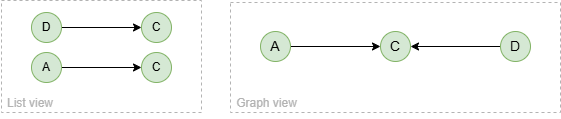
When node E is excluded, it is equivalent to removing node E and all its connected edges from the graph.
Filtering Edges
To spread from nodes A, B with 2 steps, while only traversing edges where the weight exceeds 1:
spread().src({_id in ["A", "B"]}).depth(2).edge_filter({weight > 1}) as p
return p
Result: p
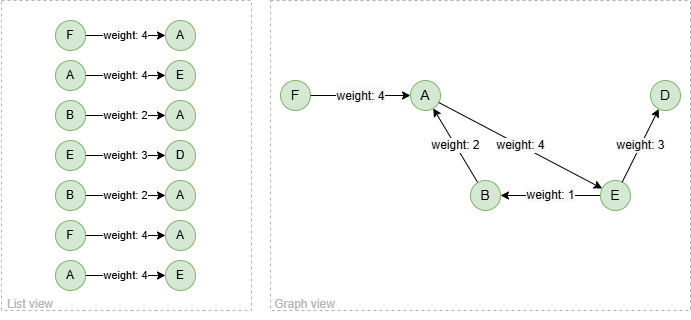
When edges with a weight below 1 are excluded, it is equivalent to removing those edges from the graph.
Setting Spreading Direction
To spread from node B with 2 steps through outgoing edges:
spread().src({_id == "B"}).depth(2).direction(right) as p
return p
Result: p
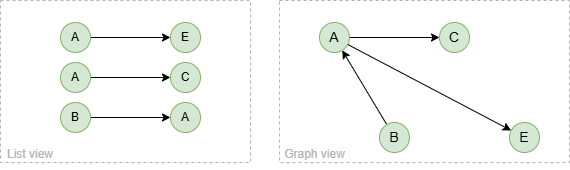
To spread from node B with 2 steps through incoming edges:
spread().src({_id == "B"}).depth(2).direction(left) as p
return p
Result: p
Although the results returned by the spread() statement are in the form of outgoing one-step paths, the direction() method constrains the search direction from nearer nodes to farther nodes.
Using limit()
To spread from nodes A, D with 2 steps, return only two paths for each traversal source:
spread().src({_id in ["A", "D"]}).depth(2).limit(2) as p
return p
Result: p
Due to the BFS nature of spreading, paths with shallower depths are returned first.
Using OPTIONAL
In this query, the spread() statement executes two times, each time using one record from n. With the OPTIONAL prefix, the query returns null if no result is found during execution:
find().nodes({_id in ["F", "G"]}) as n
OPTIONAL spread().src(n).depth(1) as p
return p
Result: p

Without the prefix OPTIONAL, only one record is returned:
find().nodes({_id in ["F", "G"]}) as n
spread().src(n).depth(1) as p
return p
Result: p