Overview
The RETURN statement allows you to specify items to include in the final output. Each item is defined by an expression that can include alias, properties, functions, constants, etc.
All UQL queries, except those for graph management, data modification, and other specific purposes, must conclude with a RETURN statement. The only statement allowed to follow a RETURN statement is the LIMIT statement, which retains a specified number of records for each return item while discarding the rest.
Syntax
RETURN <item1> as <alias1?>, <item2?> as <alias2?>, ...
Details
- The
RETURNstatement must include at least one item. - The default alias for each return item is the return item expression itself. You may rename a return item using an alias.
- In each return item expression, you can reference aliases declared in the previous statements. See Referencing Alias in RETURN for more details.
- Each return item corresponds to one the following result types:
RESULT_TYPE_NODERESULT_TYPE_EDGERESULT_TYPE_PATHRESULT_TYPE_ATTRRESULT_TYPE_TABLE
Example Graph
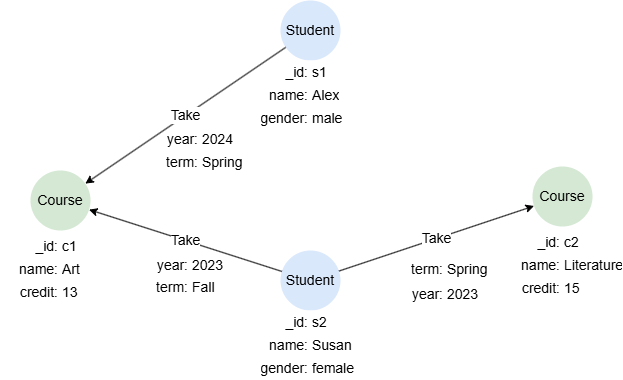
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().node_schema("Student").node_schema("Course").edge_schema("Take")
create().node_property(@Student,"name").node_property(@Student,"gender").node_property(@Course,"name").node_property(@Course,"credit",int32).edge_property(@Take, "year", int32).edge_property(@Take, "term")
insert().into(@Student).nodes([{_id:"s1", name:"Alex", gender:"male"}, {_id:"s2", name:"Susan", gender:"female"}])
insert().into(@Course).nodes([{_id:"c1", name:"Art", credit:13}, {_id:"c2", name:"Literature", credit:15}])
insert().into(@Take).edges([{_from:"s1", _to:"c1", year: 2024, term: "Spring"}, {_from:"s2", _to:"c1", year: 2023, term: "Fall"}, {_from:"s2", _to:"c2", year: 2023, term: "Spring"}])
Returning Nodes
Returns the schema and all properties of each node:
find().nodes({@Course}) as n
return n{*}
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| c1 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Art", credit: 13} |
| c2 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Literature", credit: 15} |
Returns the schema and system properties of each node:
find().nodes({@Course}) as n
return n
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema |
|---|---|---|
| c1 | Sys-gen | Course |
| c2 | Sys-gen | Course |
Returning Edges
Returns the schema and all properties of each edge:
find().edges() as e
return e{*}
Result: e
_uuid |
_from |
_to |
_from_uuid |
_to_uuid |
schema |
values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sys-gen | s2 | c1 | UUID of s2 | UUID of c1 | Take | {year: 2023, term: "Fall"} |
| Sys-gen | s2 | c2 | UUID of s2 | UUID of c2 | Take | {year: 2023, term: "Spring"} |
| Sys-gen | s1 | c1 | UUID of s1 | UUID of c1 | Take | {year: 2024, term: "Spring"} |
Returns the schema and all system properties of each edge:
find().edges() as e
return e
Result: e
| _uuid | _from | _to | _from_uuid | _to_uuid | schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sys-gen | s2 | c1 | UUID of s2 | UUID of c1 | Take |
| Sys-gen | s2 | c2 | UUID of s2 | UUID of c2 | Take |
| Sys-gen | s1 | c1 | UUID of s1 | UUID of c1 | Take |
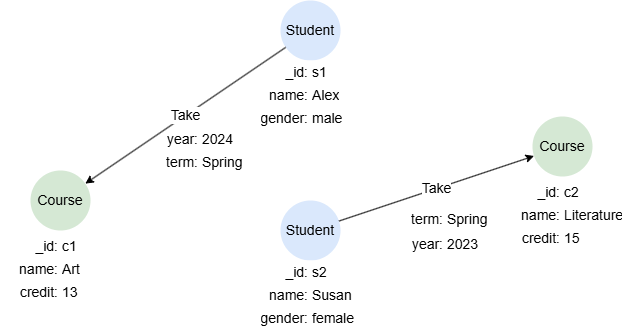
Returning Paths
Returns nodes and edges in each path (each containing its schema and all properties), along with the path length:
n().re({@Take.term == "Spring"}).n() as p
return p{*}
Result:
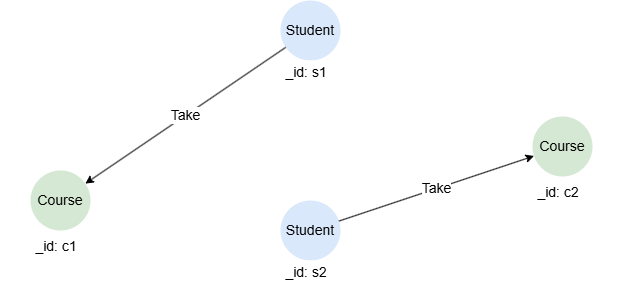
Returns nodes and edges in each path (each containing its schema and system properties), along with the path length:
n().re({@Take.term == "Spring"}).n() as p
return p
Result:
Returning Schemas
n({_id == "s2"}).e(as e).n(as n)
return e.@, n.@
Result:
| e.@ | n.@ |
|---|---|
| Take | Course |
| Take | Course |
Returning Properties
The period operator . can be used to extract the value of a specified property from an alias representing nodes or edges. The null value will be returned if the specified property is not found on the nodes or edges.
n({@Student.name == "Susan"}).re().n({@Course} as c)
return c.name, c.credit, c.type
Result:
| c.name | c.credit | c.type |
|---|---|---|
| Literature | 15 | null |
| Art | 13 | null |
You can also use a pair of curly braces {} to extract multiple properties from nodes, edges, or paths. See Referencing Alias in RETURN for more details.
n({@Student.name == "Susan"}).re().n({@Course} as c)
return c{name, credit}
Result: c
| _id | _uuid | name | credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| c1 | Sys-gen | Literature | 15 |
| c2 | Sys-gen | Art | 13 |
Returning Tables
The table() function can be used to construct an output table by specifying return items as columns.
n({@Student} as s).re().n({@Course} as c)
return table(s.name, c.name)
Result:
| s.name | c.name |
|---|---|
| Susan | Art |
| Susan | Literature |
| Alex | Art |
Return Item Alias
n({@Student} as s).re(as t).n({@Course} as c)
return s.name as Student, c.name as Course, t.year as TakenIn
Result:
| Student | Course | TakenIn |
|---|---|---|
| Alex | Art | 2024 |
| Susan | Art | 2023 |
| Susan | Literature | 2023 |
Returning Distinct Records
The DISTINCT operator can be used to deduplicate records.
n().e(as e).n()
return distinct e.year
Result:
| e.year |
|---|
| 2023 |
| 2024 |
Returning with Aggregation
Aggregation functions, such as sum() and max(), can be directly applied in the RETURN statement.
n({@Student.name == "Susan"}).re().n({@Course} as c)
return sum(c.credit)
Result:
| sum(c.credit) |
|---|
| 28 |
Returning by CASE
The CASE function can be directly applied in the RETURN statement.
n({@Course} as n)
return n.name as Course, case when n.credit > 14 then "Y" else "N" end as Recommended
Result:
| Course | Recommended |
|---|---|
| Art | N |
| Literature | Y |
Returning Limited Records
The LIMIT statement can be used to restrict the number of records returned.
find().nodes({@Course}) as n
return n.name limit 1
Result:
| n.name |
|---|
| Art |
Returning Ordered Records
The ORDER BY statement can be used to sort the records according to the specified values. It must appear before the RETURN statement in a query.
n({@Course} as n)
order by n.credit desc
return n{*}
Result: n
| _id | _uuid | schema | values |
|---|---|---|---|
| c2 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Literature", credit: 15} |
| c1 | Sys-gen | Course | {name: "Art", credit: 13} |
Returning Heterologous Data
If aliases referenced in the RETURN statement are heterologous, a Cartesian product is performed between them. See Heterologous Data for details.
find().nodes({@Course}) as c
find().nodes({@Student}) as s
return c.name, s.name
Result:
| c.name | s.name |
|---|---|
| Literature | Susan |
| Literature | Alex |
| Art | Susan |
| Art | Alex |
Referencing Alias in RETURN
NODE Type
find().nodes({@city}) as n
return n
The alias n is of the NODE type, below are more examples of referencing it in the RETURN statement:
Referencing Format |
Data Returned for Each Record | Result Type |
|---|---|---|
n |
Node schema and system properties (_id, _uuid). |
RESULT_TYPE_NODE |
n{*} |
Node schema and all properties. | RESULT_TYPE_NODE |
n.name |
Node property name. |
RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
n{name, age} |
Node schema, system properties, and properties name, age. |
RESULT_TYPE_NODE |
n.@ |
Node schema. | RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
EDGE Type
find().edges({@transfers}) as e
return e
The alias e is of the EDGE type, below are more examples of referencing it in the RETURN statement:
Referencing Format |
Data Returned for Each Record | Result Type |
|---|---|---|
e |
Edge schema and system properties (_uuid, _from, _to, _from_uuid, _to_uuid). |
RESULT_TYPE_EDGE |
e{*} |
Edge schema and all properties. | RESULT_TYPE_EDGE |
e.time |
Edge property time. |
RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
e{time, amount} |
Edge schema, system properties, and properties time, amount. |
RESULT_TYPE_EDGE |
e.@ |
Edge schema. | RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
PATH Type
n().e()[:5].n() as p
return p
The alias p is of the PATH type, below are more examples of referencing it in the RETURN statement:
Referencing Format |
Data Returned for Each Record | Result Type |
|---|---|---|
p |
Nodes and edges in the path (each containing its schema and system properties), along with the path length. | RESULT_TYPE_PATH |
p{*} |
Nodes and edges in the path (each containing its schema and all properties), along with the path length. | RESULT_TYPE_PATH |
p{name}{time, amount} |
Nodes and edges in the path (each node contains its schema, system properties, and property name; each edge contains its schema, system properties, and properties time and amount), along with the path length. |
RESULT_TYPE_PATH |
p{*}{time, amount} |
Nodes and edges in the path (each node contains its schema and all properties; each edge contains its schema, system properties, and properties time and amount), along with the path length. |
RESULT_TYPE_PATH |
p{name}{*} |
Nodes and edges in the path (each node contains its schema, system properties, and property name; each edge contains its schema and all properties), along with the path length. |
RESULT_TYPE_PATH |
p{name} |
Nodes and edges in the path (each containing its schema, system properties, and property name), along with the path length. |
RESULT_TYPE_PATH |
List Type
uncollect [[1,2,3,4,5], [4,5,6,7,8]] as lists
return lists
Each record represented by the alias lists is of the list type, below are more examples of referencing it in the RETURN statement:
Referencing Format |
Data Returned for Each Record | Result Type |
|---|---|---|
lists |
A list. | RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
lists[2] |
The 3rd element in the list. | Depends on the element type; in this case, RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
lists[0:3] |
A new list formed by the 1st to 4th elements in the original list. | RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
lists[:5] |
A new list formed by the 1st to 6th elements in the original list. | RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
lists[2:] |
A new list formed by the 3rd elements to the end in the original list. | RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
Point Type
find().nodes({@city}) as n
with n.location as points
return points
The property location is of the point type, the alias points is defined to represent the location property, below are more examples of referencing it in the RETURN statement:
Referencing Format |
Data Returned for Each Record | Result Type |
|---|---|---|
points |
A data with two coordinates, e.g., POINT(25 33) |
RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
points.x |
Value of the x coordinate | RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
points.y |
Value of the y coordinate | RESULT_TYPE_ATTR |
Other Atomic Types
Atomic types, or fundamental data types, such as integers, decimals, and strings, these types cannot be broken down into smaller components. An alias of an atomic type can only be referenced directly, as no information can be extracted from the data it represents.
find().nodes({@city}) as n
with n.name as names
return upper(names)

