Overview
A path template n()...n() defines a specific structure of paths, with node and edge templates chained in sequence. A path template retrieves paths from the graph that match the described pattern or structure.
Node and Edge Templates
Node and edge templates serve as building blocks for constructing path templates. There are four node and edge templates:
Template |
Name |
Description | Alias Type |
|---|---|---|---|
n() |
Single-node | Represents a single node in a path:  |
NODE |
e(), le(), re() |
Single-edge (Direction: both, left, right) |
Represents a single edge in a path: 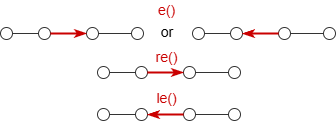 |
EDGE |
e()[<steps>],le()[<steps>],re()[<steps>] |
Multi-edge (Direction: both, left, right) |
Represents multiple consecutive edges in a path: 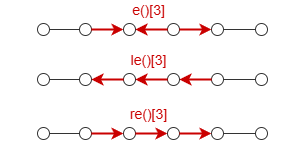 [<steps>] (N≥0):
0 is involved, it is valid only if the node preceding the edge template can be merged with the node following it. In such cases, the edge template is ignored, and the two nodes on either side are considered a single node. |
N/A |
e().nf()[<steps>],le().nf()[<steps>],re().nf()[<steps>] |
Multi-edge with intermediates (Direction: both, left, right) |
Represents multiple consecutive edges and nodes between them in a path: 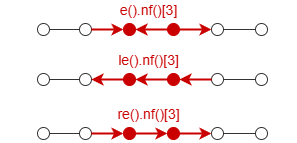 [<steps>] is the same as multi-edge template. |
N/A |
Filters enclosed in {} can be used inside the parentheses of node and edge templates to specify their schema and properties. Additionally, the first single-node template n() in a path template allows direct referencing of an alias.
Constructing Path Templates
A path begins and ends with a node, alternating between nodes and edges throughout. Notably, a path can also consist of a single node without any edges. By following this rule, you can construct the path template to suit the specific scenario. The following are some examples.
To find books recommended by users whom Kavi likes:
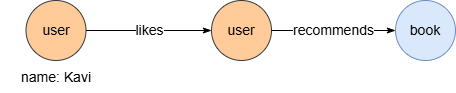
n({@user.name == "Kavi"}).re({@likes}).n({@user}).re({@recommends}).n({@books} as b)
return b.name
To find 1 to 3 step outgoing transaction paths from accounts owned by C34 to accounts owned by C135:
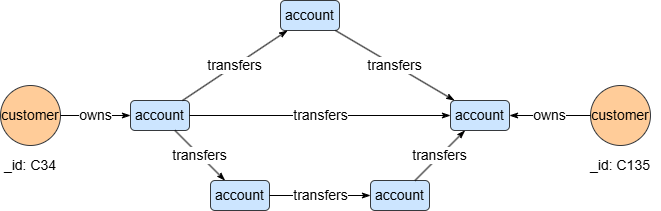
n({_id == "C34"}).re({@owns}).n({@account}).re({@transfers})[3].n({@account}).le({@owns}).n({_id == "C135"}) as p
return p{*}
To find 3-step transaction paths from accounts owned by C34 to accounts owned by C135, where intermediate accounts have a level greater than 4:
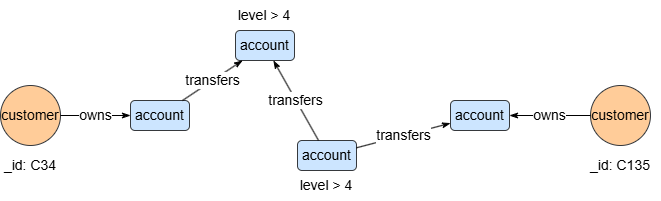
n({_id == "C34"}).re({@owns}).n({@account}).e({@transfers}).nf({@account.level > 4})[:3].n({@account}).le({@owns}).n({_id == "C135"}) as p
return p{*}
To find circular task dependency paths within 3 to 5 steps:
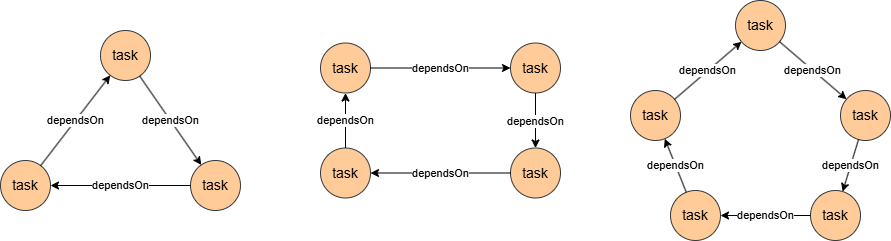
n({@task} as t).re({@dependsOn})[3:5].n({_id == t._id}) as p
return p{*}
This query reuses the alias t in the path template to form a ring-like structure.
Syntax
- Statement alias: Type
PATH - Methods that can be chained after the path template:
Method |
Param |
Description | Optional |
Alias Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
no_circle() |
/ | Excludes paths that form circles. A path has circles when it has repeated nodes. | Yes | N/A |
limit() |
<N> |
Limits the number of paths (N≥-1) returned for each start node; -1 includes all paths. |
Yes | N/A |
Example Graph 1
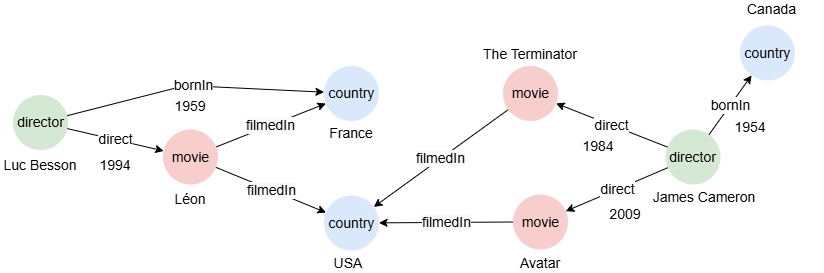
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().node_schema("country").node_schema("movie").node_schema("director").edge_schema("filmedIn").edge_schema("direct").edge_schema("bornIn")
create().node_property(@*, "name").edge_property(@direct, "year", int32).edge_property(@bornIn, "year", int32)
insert().into(@country).nodes([{_id:"C1", name:"France"}, {_id:"C2", name:"USA"}, {_id:"C3", name:"Canada"}])
insert().into(@movie).nodes([{_id:"M1", name:"Léon"}, {_id:"M2", name:"The Terminator"}, {_id:"M3", name:"Avatar"}])
insert().into(@director).nodes([{_id:"D1", name:"Luc Besson"}, {_id:"D2", name:"James Cameron"}])
insert().into(@filmedIn).edges([{_from:"M1", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"M1", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"M2", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"M3", _to:"C2"}])
insert().into(@direct).edges([{_from: "D1", _to: "M1", year: 1994}, {_from: "D2", _to: "M2", year: 1984}, {_from: "D2", _to: "M3", year: 2009}])
insert().into(@bornIn).edges([{_from: "D1", _to: "C1", year: 1959}, {_from: "D2", _to: "C3", year: 1954}])
Finding Nodes
You can declare alias in the single-node template n().
To find @movie nodes:
n({@movie} as m)
return m.name
Result:
| m.name |
|---|
| The Terminator |
| Léon |
| Avatar |
To find countries where the movie Léon was filmed:
n({@movie.name == "Léon"}).e({@filmedIn}).n(as c)
return c.name
Result:
| c.name |
|---|
| France |
| USA |
Finding Edges
You can declare alias in the single-edge template e().
To find when the movie The Terminator was directed:
n({@movie.name == "The Terminator"}).e({@direct} as d).n()
return d.year
Result:
| d.year |
|---|
| 1984 |
Finding Fixed Length Paths
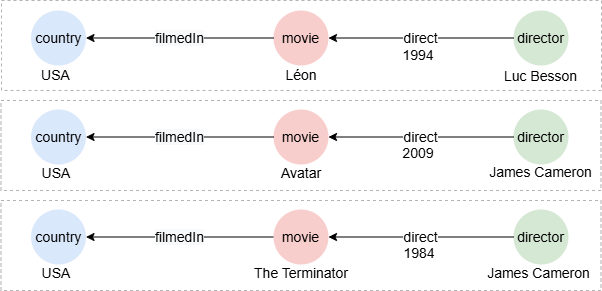
To find paths describing all movies filmed in USA along with their directors:
n({@country.name == "USA"}).le().n({@movie}).e().n({@director}) as p
return p{*}
Result: p
To find 2-step connections between movies Léon and The Terminator:
n({@movie.name == "Léon"}).e()[2].n({@movie.name == "The Terminator"}) as p
return p{*}
Result: p

Finding Variable Length Paths
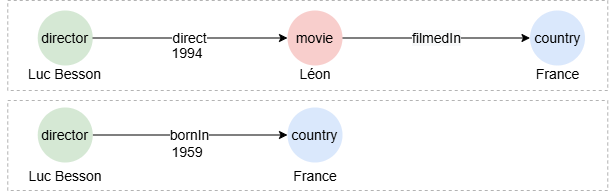
To find paths within 4 steps between Luc Besson and France:
n({name == "Luc Besson"}).e()[:4].n({name == "France"}) as p
return p{*}
Result:p
To find paths within 4 steps between Luc Besson and France that do not pass through the movie Léon:
n({name == "Luc Besson"}).e().nf({name != "Léon"})[:4].n({name == "France"}) as p
return p{*}
Result: p

Finding Shortest Paths
To find the shortest paths within 4 steps between Luc Besson and France:
n({name == "Luc Besson"}).e()[*:4].n({name == "France"}) as p
return p{*}
Result: p

Excluding Circles
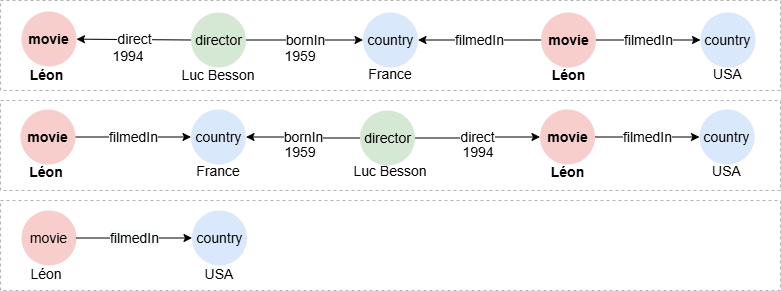
To find paths within 4 steps between Léon and USA:
n({name == "Léon"}).e()[:4].n({name == "USA"}) as p
return p{*}
Result: p
To find paths within 4 steps between Léon and USA without any circles:
n({name == "Léon"}).e()[:4].n({name == "USA"}).no_circle() as p
return p{*}
Result: p

Using limit()
To find one movie directed by each director:
n({@director} as d).e().n({@movie} as m).limit(1)
return table(d.name,m.name)
Result:
| d.name | m.name |
|---|---|
| James Cameron | The Terminator |
| Luc Besson | Léon |
Using OPTIONAL
In this query, the path template statement executes three times, each time using one record from c. With the OPTIONAL prefix, the query returns null if no result is found during execution:
find().nodes({@country}) as c
optional n(c).e({@filmedIn}).n({@movie} as m)
return table(c.name, m.name)
Result:
| c.name | m.name |
|---|---|
| France | Léon |
| Canada | null |
| USA | Léon |
| USA | Avatar |
| USA | The Terminator |
Without the prefix OPTIONAL, no record is returned for Canada:
find().nodes({@country}) as c
n(c).e({@filmedIn}).n({@movie} as m)
return table(c.name, m.name)
Result:
| c.name | m.name |
|---|---|
| France | Léon |
| USA | Léon |
| USA | Avatar |
| USA | The Terminator |
Example Graph 2
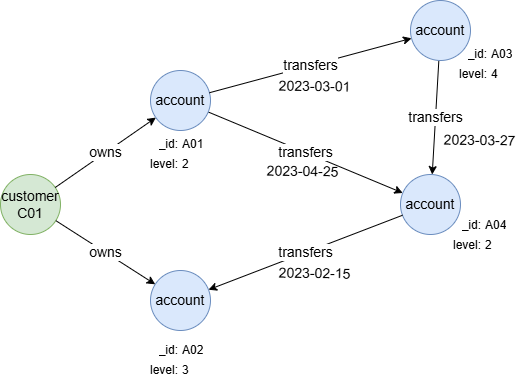
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().node_schema("customer").node_schema("account").edge_schema("owns").edge_schema("transfers")
create().node_property(@account, "level", uint32).edge_property(@transfers, "time", datetime)
insert().into(@customer).nodes([{_id:"C01"}])
insert().into(@account).nodes([{_id:"A01", level: 2}, {_id:"A02", level: 3}, {_id:"A03", level: 4}, {_id:"A04", level: 2}])
insert().into(@owns).edges([{_from:"C01", _to:"A01"}, {_from:"C01", _to:"A02"}])
insert().into(@transfers).edges([{_from:"A01", _to:"A03", time:"2023-03-01"}, {_from:"A01", _to:"A04", time:"2023-04-25"}, {_from:"A03", _to:"A04", time:"2023-03-27"}, {_from:"A04", _to:"A02", time:"2023-02-15"}])
Including 0 Step
To find 0 to 1 step outgoing transaction paths from accounts held by C01 to other accounts with a level no less than 3:
n({_id == "C01"}).e().n({@account}).re({@transfers})[0:1].n({@account.level >= 3}) as p
return p
Result: p
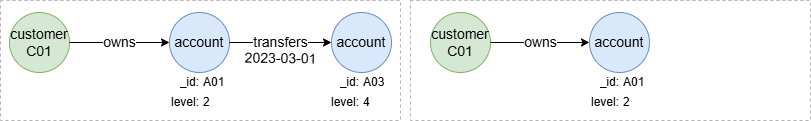
The [0:1] specifies that the traversal can include 0 or 1 step through the re({@transfers}) relationship. When the step 0 is applied, the re({@transfers})[0:1] is effectively ignored, merging the nodes before and after, and the path template simplifies to n({_id == "C01"}).e().n({@account.level >= 3}).
In the following query, the merged node n({@account.level < 3 && @account.level >= 3}) does not exist, thus the step 0 will not yield any result:
n({_id == "C01"}).e().n({@account.level < 3}).re({@transfers})[0:1].n({@account.level >= 3}) as p
return p
Result: p
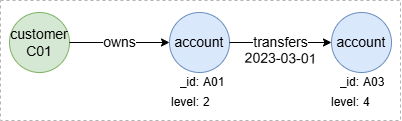
Inter-Step Filtering
prev_n, prev_e
The system aliases prev_n and prev_e facilitate inter-step filtering in path templates by allowing reference to the previous node or edge at each step.
To find 2-step outgoing transaction paths between accounts with the ascending time:
n().re({@transfers.time > prev_e.time})[2].n() as p
return p
Result: p
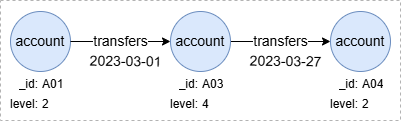
For more details on using prev_e and prev_n, refer to System Alias.
Reusing Alias
This query achieves the same as above by reusing the alias declared in the path template:
n().re({@transfers} as t1).n().re({@transfers.time > t1.time}).n() as p
return p
Result: p


