Overview
The khop().src().depth() statement retrieves K-hop neighbors of nodes.
The K-hop neighbors of a node are the nodes located at a shortest distance of K from that node. The shortest distance is defined as the number of edges included in the shortest path. In graph theory, a hop is when a node travels to another node via an edge.
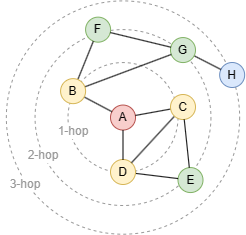
In this graph, nodes {B, C, D} are the 1-hop neighbors of node A, {E, F, G} are the 2-hop neighbors, and {H} is the 3-hop neighbor.
There are some key features regarding the K-hop neighbors:
- First,
Kis determined solely by the shortest distance and it is unique. For example, there are many paths between nodesAandC(e.g.,A-C,A-D-C,A-D-E-C), the shortest distance is1. NodeCwill only appear as a 1-hop neighbor ofAand will not be included in results for other K-hop queries. - Second, the K-hop query results are deduplicated. For example, although there are two shortest paths between nodes
AandE(A-C-EandA-D-E),Ewill only appear once in the 2-hop query results of nodeA.
The K-hop query adopts the breadth first search (BFS) technique to find the shortest paths and the K-hop neighbors. Optimizations have been applied in Ultipa to improve the performance of the K-hop query. It's recommended to use the K-hop query instead of other path query methods for the same purpose.
Syntax
khop().src(<filter?>).depth(<range>)
- Statement alias: Type
NODE - Methods:
Method |
Param |
Description | Optional |
Alias Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
src() |
<filter?> |
The filtering condition enclosed in {}, or an alias to specify the set of nodes as traversal sources. Leaving it blank will target all nodes. |
No | NODE |
depth() |
<range> |
The value of K (N≥0):
0 is involved, it returns the traversal source node along with its K-hop neighbors. |
No | N/A |
node_filter() |
<filter?> |
The filtering condition enclosed in {} for neighbor nodes. Leaving it blank applies no restriction. |
Yes | N/A |
edge_filter() |
<filter?> |
The filtering condition enclosed in {} for edges in the shortest paths. Leaving it blank applies no restriction. |
Yes | N/A |
direction() |
<leftRight> |
Specifies the direction of all edges in the shortest paths, which can be left or right. |
Yes | N/A |
limit() |
<N> |
Limits the number of K-hop neighbors (N≥-1) returned for each traversal source; -1 includes all. |
Yes | N/A |
Example Graph
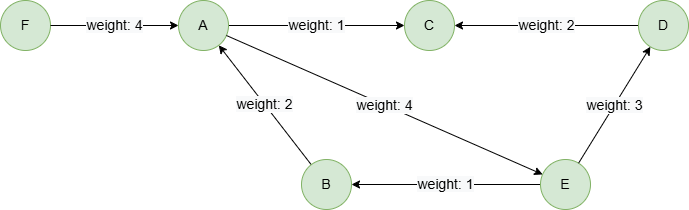
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().edge_property(@default, "weight", int32)
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}])
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"C", weight:1}, {_from:"E", _to:"B", weight:1}, {_from:"A", _to:"E", weight:4}, {_from:"D", _to:"C", weight:2}, {_from:"E", _to:"D", weight:3}, {_from:"B", _to:"A", weight:2}, {_from:"F", _to:"A", weight:4}])
Finding K-Hop Neighbors
Within N Hops
To find 1 to 3-hop neighbors of node D:
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(1:3) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["E","C","B","A","F"] |
Exact N Hops
To find 3-hop neighbors of node D:
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(3) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["F"] |
Within N to M Hops
To find 2 to 3-hop neighbors of node D:
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(2:3) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["B","A","F"] |
Filtering Neighbors
To find 3-hop neighbors of node D while excluding node E:
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(3).node_filter({_id != "E"}) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["F","B"] |
When node E is excluded, it is equivalent to removing node E and all its connected edges from the graph. As a result, the shortest path structure of the graph changes, and node B becomes the 3-hop neighbor of D.
Filtering Edges
To find 1-hop neighbors of nodes A, D while excluding edges with a weight exceeds 3:
khop().src({_id in ["A", "D"]} as src).depth(1).edge_filter({weight <= 3}) as n
group by src
return src._id, count(n)
Result:
| src._id | count(n) |
|---|---|
| D | 2 |
| A | 2 |
When edges with a weight exceeds 3 are excluded, it is equivalent to removing those edges from the graph. As a result, the shortest path structure of the graph changes.
Setting Edge Directions
To find 1- to 2-hop neighbors of node D where all edges in the traversing shortest paths point to the right:
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(:2).direction(right) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["C"] |
Returning Source Node
To find 1-hop neighbors of node D and return node D at the same time:
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(0:1) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["D","E","C"] |
Using limit()
To find 1- to 2-hop neighbors of nodes A and D, return only one for each:
khop().src({_id in ["D", "A"]}).depth(:2).limit(1) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["E","F"] |
Due to the BFS nature of the K-hop query, neighbors that are closer to the source node (i.e., at lower hops) are returned first.
Using OPTIONAL
In this query, the khop() statement executes two times, each time using one record from start. With the OPTIONAL prefix, the query returns null if no result is found during execution:
find().nodes({_id in ["A", "D"]}) as start
optional khop().src(start).depth(2).direction(right) as n
return table(start._id, n._id)
Result:
| start._id | n._id |
|---|---|
| D | null |
| A | D |
| A | B |
Without the prefix OPTIONAL, no record is returned for node D:
find().nodes({_id in ["A", "D"]}) as start
khop().src(start).depth(2).direction(right) as n
return table(start._id, n._id)
Result:
| start._id | n._id |
|---|---|
| A | D |
| A | B |

