Overview
The HITS (Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search) algorithm was developed by L.M. Kleinberg in 1999 with the purpose of improving the quality of search methods on the World Wide Web (WWW). HITS makes use of the mutual reinforcing relationship between authorities and hubs to evaluate and rank a set of linked entities.
- L.M. Kleinberg, Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Environment (1999)
Concepts
Authority and Hub
In WWW, hyperlinks represent some latent human judgment: the creator of page p, by including a link to page q, has in some measure conferred authority on q. Instructively, a node with large in-degree is viewed as an authority.
If a node points to a considerable number of authoritative nodes, it is referred to as a hub.
As illustrated in the graph below, red nodes represent good authorities, while green nodes represent good hubs.
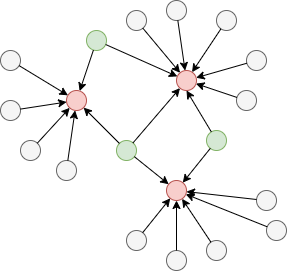
Hubs and authorities exhibit a mutually reinforcing relationship: a good hub points to many good authorities; a good authority is pointed to by many good hubs.
Compute Authorities and Hubs
HITS algorithm operates on the whole graph iteratively to compute the authority weight (denoted as x) and hub weight (denoted as y) for each node through the link structure. Nodes with larger x-values and y-values are viewed as better authorities and hubs respectively.
In a directed graph G = (V, E), all nodes are initialized with x = 1 and y = 1. In each iteration, for each node p ∈ V, update its x and y values as follows:
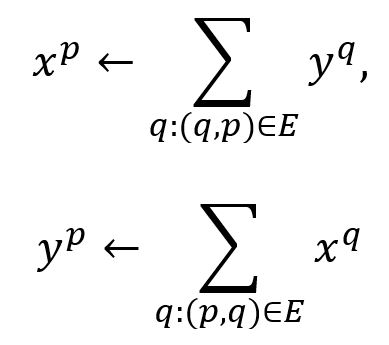
Here is an example:
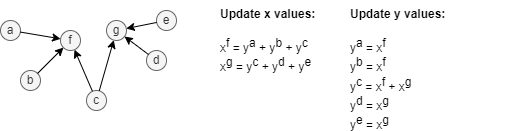
At the end of one iteration, normalize all x values and all y values to meet the invariant below:
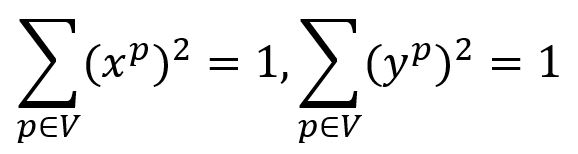
The algorithm iterates until the changes in all x and y values converge within a specific tolerance, or until the maximum number of iterations is reached. In the experiments of the original author, the convergence is quite rapid, 20 iterations are normally sufficient.
Considerations
- In HITS algorithm, self-loops are ignored.
- Nodes with no in-links are assigned an authority weight of 0, while nodes with no out-links are assigned a hub weight of 0.
Example Graph
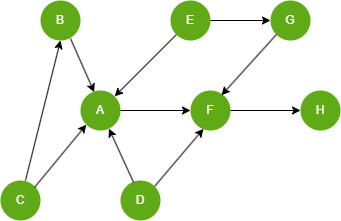
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A"}),
(B:default {_id: "B"}),
(C:default {_id: "C"}),
(D:default {_id: "D"}),
(E:default {_id: "E"}),
(F:default {_id: "F"}),
(G:default {_id: "G"}),
(H:default {_id: "H"}),
(A)-[:default]->(F),
(B)-[:default]->(A),
(C)-[:default]->(A),
(C)-[:default]->(B),
(D)-[:default]->(A),
(D)-[:default]->(F),
(E)-[:default]->(A),
(E)-[:default]->(G),
(F)-[:default]->(H),
(G)-[:default]->(F);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}, {_id:"G"}, {_id:"H"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"C", _to:"A"}, {_from:"C", _to:"B"}, {_from:"B", _to:"A"}, {_from:"E", _to:"A"}, {_from:"E", _to:"G"}, {_from:"A", _to:"F"}, {_from:"D", _to:"A"}, {_from:"D", _to:"F"}, {_from:"F", _to:"H"}, {_from:"G", _to:"F"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: hits_centrality
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
max_loop_num |
Integer | ≥1 | 20 |
Yes | The maximum number of iteration rounds. The algorithm will terminate after completing all rounds. |
tolerance |
Float | (0,1) | 0.001 |
Yes | The algorithm terminates when the changes in all authority and hub weights between iterations are less than the specified tolerance, indicating that the result is stable. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both values to represent nodes in the results. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.hits_centrality.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id"
}, {
file: {
filename: "ranks"
}
})
algo(hits_centrality).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
projection: "my_hdc_graph"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "ranks"
}
})
Result:
_id,authority,hub
D,0,0.572083
F,0.42642,1.43197e-11
H,3.20199e-11,0
B,0.213196,0.381382
A,0.852796,0.190701
E,0,0.476726
C,0,0.476726
G,0.213196,0.190701
DB Writeback
Writes the authority and hub values from the results to the specified node property. The property types are both double.
CALL algo.hits_centrality.write("my_hdc_graph", {
max_loop_num: 20,
tolerance: 0.0001
}, {
db: {
authority: 'auth',
hub: 'hub'
}
})
algo(hits_centrality).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
max_loop_num: 20,
tolerance: 0.0001
}).write({
db: {
authority: 'auth',
hub: 'hub'
}
})
Full Return
CALL algo.hits_centrality.run("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id"
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(hits_centrality).params({
return_id_uuid: "id"
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id | authority | hub |
|---|---|---|
| D | 0 | 0.572083 |
| F | 0.42642 | 0 |
| H | 0 | 0 |
| B | 0.213196 | 0.381382 |
| A | 0.852796 | 0.190701 |
| E | 0 | 0.476726 |
| C | 0 | 0.476726 |
| G | 0.213196 | 0.190701 |
Stream Return
CALL algo.hits_centrality.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
max_loop_num: 20,
tolerance: 0.0001
}) YIELD r
RETURN r._id, r.hub ORDER BY r.hub DESC
exec{
algo(hits_centrality).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
max_loop_num: 20,
tolerance: 0.0001
}).stream() as r
return r._id, r.hub order by r.hub
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| r._id | r.hub |
|---|---|
| D | 0.572083 |
| E | 0.476726 |
| C | 0.476726 |
| B | 0.381382 |
| A | 0.190701 |
| G | 0.190701 |
| F | 0 |
| H | 0 |

