Overview
Graph traversal is a search technique used to systematically visit and explore all the nodes in a graph. Its primary goal is to reveal and examine the structure and connections of the graph. There are two common strategies for graph traversal:
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Depth-First Search (DFS)
The Depth-First Search (DFS) algorithm is based on the principle of backtracking and proceeds as follows:
- Create a stack (last-in, first-out) to keep track of visited nodes.
- Start from a selected node, push it into the stack, and mark it as visited.
- Push any unvisited neighbor of the node on the top of the stack into the stack, and mark it as visited. If multiple unvisited neighbors exist, select one arbitrarily or according to a predefined order.
- Repeat step 3 until there are no more unvisited neighbors to push into the stack.
- When there are no new nodes to visit, backtrack to the previous node (the one from which the current node was explored) by popping the top node from the stack.
- Repeat steps 3, 4 and 5 until the stack is empty.
Below is an example of traversing the graph using the DFS approach, starting from node A and assuming to visit neighbors in alphabetical order (A~Z):
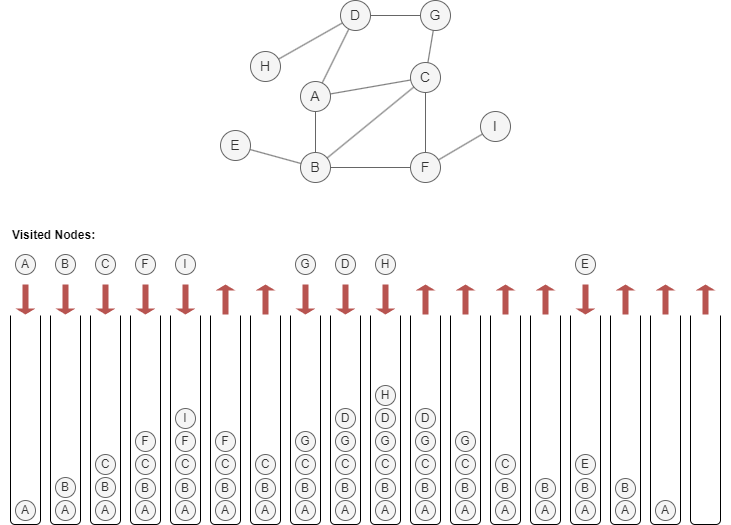
Considerations
- Only nodes within the same connected component as the start node will be traversed. Nodes in other connected components are excluded from the traversal results.
Example Graph
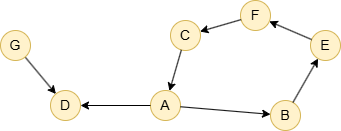
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A"}),
(B:default {_id: "B"}),
(C:default {_id: "C"}),
(D:default {_id: "D"}),
(E:default {_id: "E"}),
(F:default {_id: "F"}),
(G:default {_id: "G"}),
(A)-[:default]->(B),
(A)-[:default]->(D),
(B)-[:default]->(E),
(C)-[:default]->(A),
(E)-[:default]->(F),
(F)-[:default]->(C),
(G)-[:default]->(D);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}, {_id:"G"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"G", _to:"D"}, {_from:"A", _to:"D"}, {_from:"A", _to:"B"}, {_from:"B", _to:"E"}, {_from:"E", _to:"F"}, {_from:"F", _to:"C"}, {_from:"C", _to:"A"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: traverse
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ids |
_id |
/ | / | No | Specifies the node to start traversal by its _id. |
uuids |
_uuid |
/ | / | No | Specifies the node to start traversal by its _uuid. |
direction |
String | in, out |
/ | Yes | Specifies to traverse through only incoming edges (in) or outgoing edges (out). |
traverse_type |
String | dfs |
bfs |
No | To traverse the graph in the DFS fashion, keep it as dfs. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.traverse.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['B'],
direction: 'in',
traverse_type: 'dfs'
}, {
file: {
filename: "visited_nodes"
}
})
algo(traverse).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
ids: ['B'],
direction: 'in',
traverse_type: 'dfs'
}).write({
file: {
filename: "visited_nodes"
}
})
Result:
nodes
B,A,C,F,E,

