Overview
The Local Clustering Coefficient algorithm calculates the density of connection among the immediate neighbors of a node. It quantifies the ratio of actual connections among the neighbors to the maximum possible connections.
The local clustering coefficient provides insights into the cohesion of a node's ego network. In the context of a social network, the local clustering coefficient helps understand the degree of interconnectedness among an individual's friends or acquaintances. A high local clustering coefficient suggests that the person's friends are likely to be connected to each other, indicating the presence of a closely-knit social group, such as a family. Conversely, a low local clustering coefficient indicates a more dispersed or loosely interconnected ego network, where the person's friends do not have strong connections with each other.
Concepts
Local Clustering Coefficient
Mathematically, the local clustering coefficient of a node in an undirected graph is calculated as the ratio of the number of connected neighbor pairs to the total number of possible neighbor pairs:
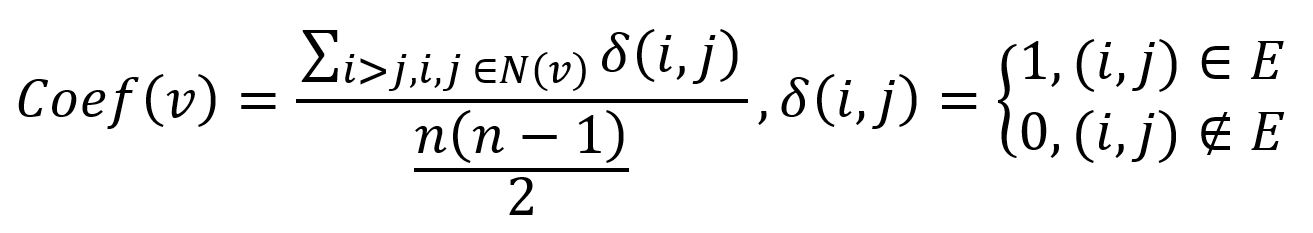
where n is the number of nodes contained in the 1-hop neighborhood of node v (denoted as N(v)), i and j are any two distinct nodes within N(v), δ(i,j) is equal to 1 if i and j are connected, and 0 otherwise.
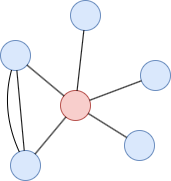
In this example, the local clustering coefficient of the red node is 1/(5*4/2) = 0.1.
Considerations
- The Local Clustering Coefficient algorithm ignores the direction of edges but calculates them as undirected edges.
Example Graph
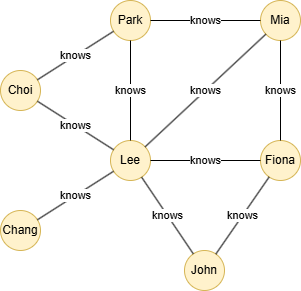
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
ALTER GRAPH CURRENT_GRAPH ADD EDGE {
knows ()-[]->()
};
INSERT (Lee:default {_id: "Lee"}),
(Choi:default {_id: "Choi"}),
(Mia:default {_id: "Mia"}),
(Fiona:default {_id: "Fiona"}),
(Chang:default {_id: "Chang"}),
(John:default {_id: "John"}),
(Park:default {_id: "Park"}),
(Choi)-[:knows]->(Park),
(Choi)-[:knows]->(Lee),
(Park)-[:knows]->(Lee),
(Park)-[:knows]->(Mia),
(Lee)-[:knows]->(Mia),
(Mia)-[:knows]->(Fiona),
(Fiona)-[:knows]->(Lee),
(Lee)-[:knows]->(Chang),
(Lee)-[:knows]->(John),
(John)-[:knows]->(Fiona);
create().edge_schema("knows");
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"Lee"}, {_id:"Choi"}, {_id:"Mia"}, {_id:"Fiona"}, {_id:"Chang"}, {_id:"John"}, {_id:"Park"}]);
insert().into(@knows).edges([{_from:"Choi", _to:"Park"}, {_from:"Choi", _to:"Lee"}, {_from:"Park", _to:"Lee"}, {_from:"Park", _to:"Mia"}, {_from:"Lee", _to:"Mia"}, {_from:"Mia", _to:"Fiona"}, {_from:"Fiona", _to:"Lee"}, {_from:"Lee", _to:"Chang"}, {_from:"Lee", _to:"John"}, {_from:"John", _to:"Fiona"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: clustering_coefficient
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ids |
[]_id |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies nodes for computation by their _id. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
uuids |
[]_uuid |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies nodes for computation by their _uuid. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned; -1 includes all results. |
order |
String | asc, desc |
/ | Yes | Sorts the results by local clustering coefficient clce_centrality. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.clustering_coefficient.write("my_hdc_graph", {
ids: ["Lee", "Choi"],
return_id_uuid: "id"
}, {
file: {
filename: "lcc"
}
})
algo(clustering_coefficient).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
ids: ["Lee", "Choi"],
return_id_uuid: "id"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "lcc"
}
})
Result:
_id,clce_centrality
Lee,0.266667
Choi,1
DB Writeback
Writes the clce_centrality values from the results to the specified node property. The property type is float.
CALL algo.clustering_coefficient.write("my_hdc_graph", {}, {
db: {
property: "lcc"
}
})
algo(clustering_coefficient).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph"
}).write({
db: {
property: "lcc"
}
})
Full Return
CALL algo.clustering_coefficient.run("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
order: "desc"
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(clustering_coefficient).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
order: "desc"
}) as result
return result
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id | clce_centrality |
|---|---|
| John | 1 |
| Choi | 1 |
| Park | 0.666667 |
| Fiona | 0.666667 |
| Mia | 0.666667 |
| Lee | 0.266667 |
| Chang | 0 |
Stream Return
CALL algo.clustering_coefficient.stream("my_hdc_graph", {}) YIELD r
FILTER r.clce_centrality = 1
RETURN count(r)
exec{
algo(clustering_coefficient).params().stream() as r
where r.clce_centrality == 1
return count(r)
} on my_hdc_graph
Result: 2

