Overview
A graph pattern is composed of three parts:
- Match Mode (Optional)
- Path Pattern List
WHEREClause (Optional)
<graph pattern> ::=
[ <match mode> ] <path pattern list> [ <where clause> ]
<path pattern list> ::=
<path pattern> [ { "," <path pattern> }... ]
The path pattern list consists of one or multiple path patterns. Each path pattern is independently matched against the graph, producing a result set. These sets are either equi-joined on the common variables (if any exist) or combined using the Cartesian product.
Example Graph
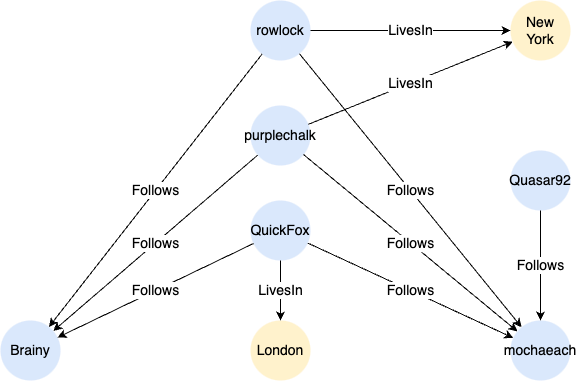
CREATE GRAPH myGraph {
NODE User ({name string}),
NODE City ({name string}),
EDGE Follows ()-[]->(),
EDGE LivesIn ()-[]->()
} SHARDS [1]
INSERT (brainy:User {_id: "U01", name: "Brainy"}),
(rowlock:User {_id: "U02", name: "rowlock"}),
(purplechalk:User {_id: "U03", name: "purplechalk"}),
(quickfox:User {_id: "U04", name: "QuickFox"}),
(quasar92:User {_id: "U05", name: "Quasar92"}),
(mochaeach:User {_id: "U06", name: "mochaeach"}),
(london:City {_id: "C01", name: "London"}),
(newyork:City {_id: "C02", name: "New York"}),
(rowlock)-[:Follows]->(brainy),
(purplechalk)-[:Follows]->(brainy),
(quickfox)-[:Follows]->(brainy),
(rowlock)-[:Follows]->(mochaeach),
(purplechalk)-[:Follows]->(mochaeach),
(quickfox)-[:Follows]->(mochaeach),
(quasar92)-[:Follows]->(mochaeach),
(quickfox)-[:LivesIn]->(london),
(rowlock)-[:LivesIn]->(newyork),
(purplechalk)-[:LivesIn]->(newyork)
Connected Paths
To get common followers of Brainy and mochaeach who live in New York:
MATCH ({name: 'Brainy'})<-[:Follows]-(u:User)-[:Follows]->({name: 'mochaeach'}),
(u)-[:LivesIn]->({name: 'New York'})
RETURN u.name
The two path patterns in MATCH declare a common variable u. An equi-join is performed, joining rows where the values of u are equal and discarding the rest.
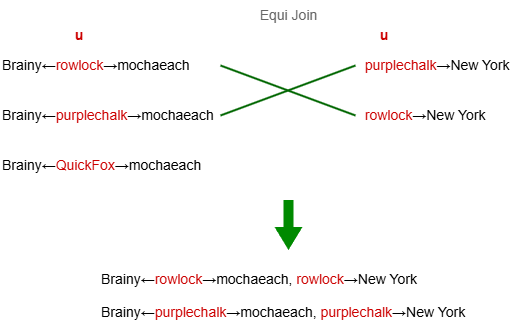
Result:
| u.name |
|---|
| rowlock |
| purplechalk |
Disconnected Paths
Consider this query:
MATCH (u1:User)-[:Follows]->({name: 'Brainy'}),
(u2:User)-[:LivesIn]->({name: 'New York'})
RETURN u1.name, u2.name
The two path patterns in MATCH declare no common variables, resulting in a Cartesian product. Each row from the first result set is combined with every row from the second.
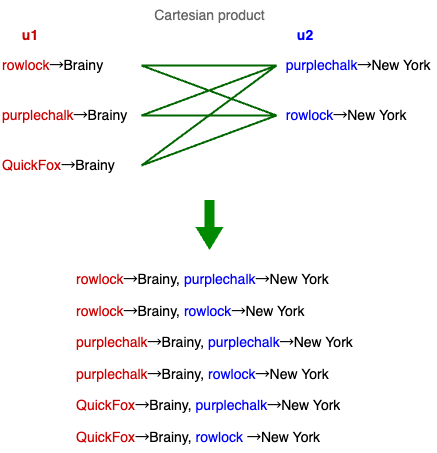
Result:
| u1.name | u2.name |
|---|---|
| rowlock | rowlock |
| rowlock | purplechalk |
| purplechalk | rowlock |
| purplechalk | purplechalk |
| QuickFox | rowlock |
| QuickFox | purplechalk |
Please note that Cartesian products often lead to unintended results and can significantly increase query overhead when dealing with large datasets. Therefore, unless explicitly required, it's best to avoid Cartesian products when writing queries.
Match Mode
A graph pattern can specify a match mode that applies to all contained path patterns. There are two match modes:
Match Mode |
Description |
|---|---|
DIFFERENT EDGES |
The default. Repeated edges are not permitted in a record. There are no restrictions on nodes. |
REPEATABLE ELEMENTS |
It is non-restrictive. |
The
REPEATABLE ELEMENTSis not supported yet.
Example Graph
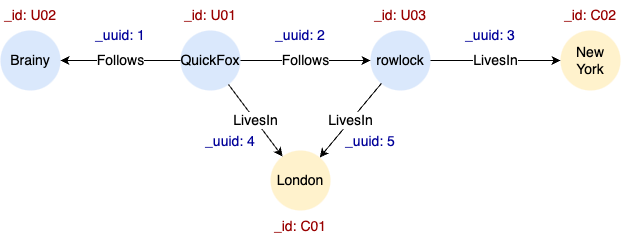
CREATE GRAPH myGraph {
NODE User ({name string}),
NODE City ({name string}),
EDGE Follows ()-[]->(),
EDGE LivesIn ()-[]->()
} SHARDS [1]
INSERT (quickfox:User {_id: "U01", name: "QuickFox"}),
(brainy:User {_id: "U02", name: "Brainy"}),
(rowlock:User {_id: "U03", name: "rowlock"}),
(london:City {_id: "C01", name: "London"}),
(newyork:City {_id: "C02", name: "New York"}),
(quickfox)-[:Follows]->(brainy),
(quickfox)-[:Follows]->(rowlock),
(rowlock)-[:LivesIn]->(newyork),
(quickfox)-[:LivesIn]->(london),
(rowlock)-[:LivesIn]->(london)
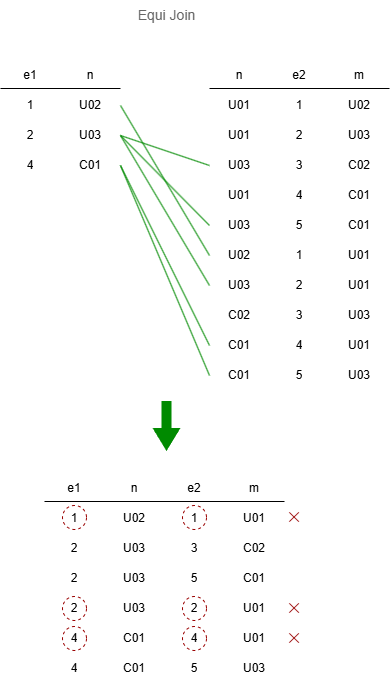
DIFFERENT EDGES
This query finds nodes connected to QuickFox, and also have other different connections:
MATCH DIFFERENT EDGES ({name: "QuickFox"})-[e1]-(n), (n)-[e2]-(m)
RETURN collect_list(n._id)
Result:
| n._id |
|---|
| ["U03","U03","C01"] |
REPEATABLE ELEMENTS
Compare the result of the query with the REPEATABLE ELEMENTS match mode:
MATCH REPEATABLE ELEMENTS ({name: "QuickFox"})-[e1]-(n), (n)-[e2]-(m)
RETURN collect_list(n._id)
Result:
| n._id |
|---|
| ["U02","U03","U03","U03","C01","C01"] |
Ensuring Unique Edge Bindings in DIFFERENT EDGES
Only records where edges are uniquely bound to different variables are retained in the DIFFERENT EDGES match mode. Therefore, if an edge variable is reused in a graph pattern, no results will be returned. See the following examples:
MATCH DIFFERENT EDGES ()-[e]->(), ()-[e]->()
RETURN e
MATCH DIFFERENT EDGES ()-[e]->()<-[e]-()
RETURN e

