Overview
The ORDER BY statement sorts records based on a set of keys. When multiple keys are provided, sorting is applied sequentially from left to right: first by the first key, then by the second key for records with identical first key values, and so on.
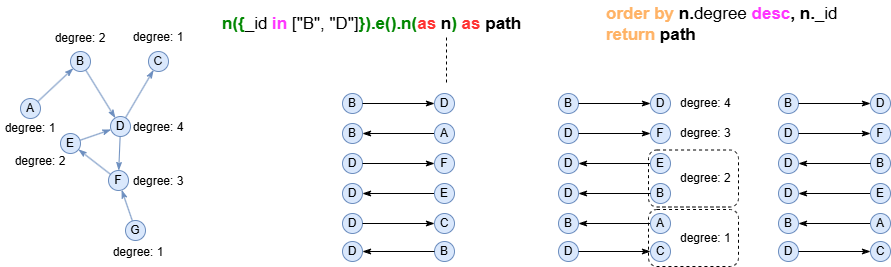
Syntax
ORDER BY <key1> <desc_asc?>, <key2?> <desc_asc?>, ...
Details
<key>: The sorting key which references an alias declared in previous statements.<desc_asc?>: The ordering specification, which isASC(ascending) orDESC(descending). It's optional andASCis applied by default.- The
nullvalues are excluded from the sorting process, and their corresponding records are placed at the end of the sorted results.
Example Graph
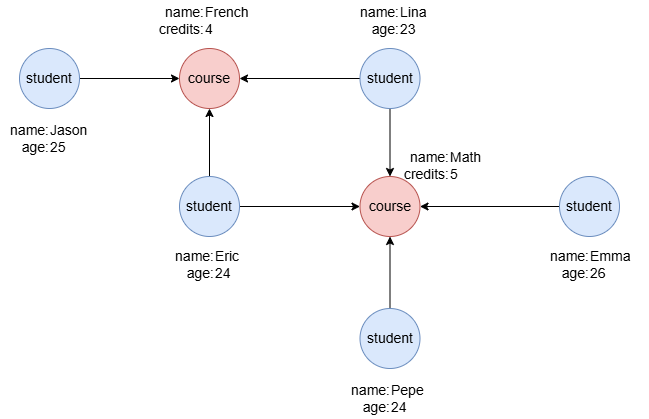
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().node_schema("student").node_schema("course").edge_schema("takes")
create().node_property(@*, "name").node_property(@student, "age", int32).node_property(@course, "credits", int32)
insert().into(@student).nodes([{_id:"S1", name:"Jason", age:25}, {_id:"S2", name:"Lina", age:23}, {_id:"S3", name:"Eric", age:24}, {_id:"S4", name:"Emma", age:26}, {_id:"S5", name:"Pepe", age:24}])
insert().into(@course).nodes([{_id:"C1", name:"French", credits:4}, {_id:"C2", name:"Math", credits:5}])
insert().into(@takes).edges([{_from:"S1", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"S2", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"S3", _to:"C1"}, {_from:"S2", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"S3", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"S4", _to:"C2"}, {_from:"S5", _to:"C2"}])
Ordering by Property
find().nodes({@student}) as stu
order by stu.age desc
return table(stu.name, stu.age)
Result:
| stu.name | stu.age |
|---|---|
| Emma | 26 |
| Jason | 25 |
| Pepe | 24 |
| Eric | 24 |
| Lina | 23 |
Ordering by Node/Edge Alias
When a node or edge alias is used as the sorting key, records are sorted by the _uuid of the corresponding nodes or edges.
find().nodes({@student}) as stu
order by stu
return table(stu.name, stu._uuid)
Result:
| stu.name | stu._uuid |
|---|---|
| Pepe | 5404321751867850754 |
| Jason | 5908724910133346305 |
| Eric | 9079259047802175489 |
| Emma | 15924730481405329410 |
| Lina | 16717364015822536705 |
Ordering by Expression
n({name == "Jason"}).e()[:3].n() as p
order by length(p)
return p{*}
Jason -> French
Jason -> French <- Lina
Jason -> French <- Eric
Jason -> French <- Lina -> Math
Jason -> French <- Eric -> Math
Multi-level Ordering
n({@course} as crs).e().n({@student} as stu) as p
order by crs.credits, stu.age desc
return table(crs.name, crs.credits, stu.name, stu.age)
Result:
| crs.name | crs.credits | stu.name | stu.age |
|---|---|---|---|
| French | 4 | Jason | 25 |
| French | 4 | Eric | 24 |
| French | 4 | Lina | 23 |
| Math | 5 | Emma | 26 |
| Math | 5 | Eric | 24 |
| Math | 5 | Pepe | 24 |
| Math | 5 | Lina | 23 |
Grouping and Ordering
To count the number of students enrolled in each course and sort the results by the count:
n({@course} as crs).e().n({@student})
group by crs
with crs, count(crs) as stuCnt
order by stuCnt desc
return table(crs.name, stuCnt)
Result:
| crs.name | stuCnt |
|---|---|
| Math | 4 |
| French | 3 |

