Overview
The K-Hop template khop().n()...n() retrieves K-hop neighbors of the first nodes in paths, following a defined path template. The value of K is determined by the length of the shortest paths that conform to the path template. Meanwhile, the returned K-hop neighbors must satisfy the condition set in the last n() in the path template.
K-Hop vs. K-Hop Template
Compared to K-Hop, the K-Hop template offers greater flexibility in defining the shortest paths used to find the K-hop neighbors:
| K-Hop | K-Hop Template | |
|---|---|---|
| Value of K | Determined by the depth() method |
Defined by the path template |
| Edge Filtering | Uniform across all edges using the edge_filter() and direction() methods |
Can vary for each edge |
| Neighbor Node Filtering | Uniform for all nodes using the node_filter() method |
Can vary for each node |
Path Template vs. K-Hop Template
While achieving the same query purpose, the K-Hop template generally offers better performance than the path template.
For example, the two queries below yield the same results - the number of distinct ads clicked by a user. However, the K-Hop template query runs more efficiently, especially on large-scale graphs.
n({_id == "u316"}).e({@clicks}).n({@ad} as ads)
return count(DISTINCT ads)
khop().n({_id == "u316"}).e({@clicks}).n({@ad}) as ads
with count(ads)
Moreover, the destination nodes returned by the path template are not deduplicated, therefore the DISTINCT is used. In contrast, the results of the K-Hop template are automatically deduplicated, ensuring each destination node is included only once, regardless of the number of paths leading to it.
Note that the type of the statement alias differs between them: For the path template, the alias type is PATH; while for the K-Hop template, the alias type is NODE.
Syntax
- Statement alias: Type
NODE - About the path template:
- The first
n()must include a valid filter enclosed in{}or an alias reference to specify the traversal sources. - The edge templates
e()[<steps>]ande().nf()[<steps>]do not support the format[*:N]for[<steps>], as the K-Hop template inherently traverses the shortest paths. - When a depth of
0is involved in[<steps>], it returns the traversal source node along with its K-hop neighbors. - Inter-step filtering is not supported, whether through system alias (
prev_n,prev_e) or by reusing alias.
- The first
- Methods that can be chained after the path template:
Method |
Param |
Description | Optional |
Alias Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
limit() |
<N> |
Limits the number of K-hop neighbors (N≥-1) returned for each start node; -1 includes. |
Yes | N/A |
Example Graph
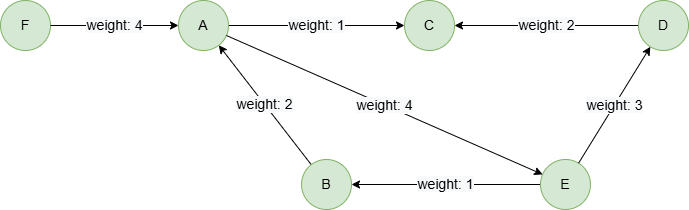
To create the graph, execute each of the following UQL queries sequentially in an empty graphset:
create().edge_property(@default, "weight", int32)
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}])
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"C", weight:1}, {_from:"E", _to:"B", weight:1}, {_from:"A", _to:"E", weight:4}, {_from:"D", _to:"C", weight:2}, {_from:"E", _to:"D", weight:3}, {_from:"B", _to:"A", weight:2}, {_from:"F", _to:"A", weight:4}])
Finding K-Hop Neighbors
Within N Hops
To find 1- to 2-hop neighbors of node A:
khop().n({_id == "A"}).e()[:2].n() as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["C","F","E","B","D"] |
Exact N Hops
To find 2-hop neighbors of node A:
khop().n({_id == "A"}).e()[2].n() as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["D"] |
Within N to M Hops
To find 2- to 3-hop neighbors of node D:
khop().n({_id == "D"}).e()[2:3].n() as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["A","B","F"] |
Filtering Neighbors
To find 2-hop neighbors of node D, where each shortest path does not pass through node C at the first step and avoids node A at the second step:
khop().n({_id == "D"}).e().n({_id != "C"}).e().n({_id != "A"}) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["B"] |
Filtering Edges
To find 2-hop neighbors of node D, where the two edges in each shortest path point to the right and left respectively:
khop().n({_id == "D"}).re().n().le().n() as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["A"] |
Returning Source Node
To find 1-hop neighbors of node D and return node D at the same time:
khop().n({_id == "D"}).e()[0:1].n() as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["D","E","C"] |
Using limit()
To find 1- to 2-hop neighbors of nodes A and D, return only one for each:
khop().n({_id in ["D", "A"]}).e()[:2].n().limit(1) as n
return collect(n._id)
Result:
| collect(n._id) |
|---|
| ["E","C"] |
Using OPTIONAL
In this query, the khop().n()...n() statement executes two times, each time using one record from start. With the OPTIONAL prefix, the query returns null if no result is found during execution:
find().nodes({_id in ["A", "D"]}) as start
optional khop().n(start).re()[2].n() as n
return table(start._id, n._id)
Result:
| start._id | n._id |
|---|---|
| D | null |
| A | D |
| A | B |
Without the prefix OPTIONAL, no record is returned for node D:
find().nodes({_id in ["A", "D"]}) as start
khop().n(start).re()[2].n() as n
return table(start._id, n._id)
Result:
| start._id | n._id |
|---|---|
| A | D |
| A | B |

