Overview
A random walk begins at a specific node in a graph and moves by randomly selecting one of its neighboring nodes at each step. This process is often repeated for a set number of steps. Introduced by British mathematician and biostatistician Karl Pearson in 1905, the concept has since become a cornerstone in studying a wide range of systems, both inside and beyond graph theory.
- K. Pearson, The Problem of the Random Walk (1905)
Concepts
Random Walk
A random walk is a mathematical model employed to simulate a sequence of steps taken in a stochastic or unpredictable manner—much like the erratic path of a drunken person.
The simplest form of a random walk occurs in one-dimensional space: a node starts at the origin of a number line and moves either one unit up or down at each step, with equal probability. An example of a 10-step random walk is shown below:
Here is an example of performing multiple random walks, each consisting of 100 steps:
Random Walk in Graph
In a graph, a random walk is a process that forms a path by starting at a node and sequentially moving to neighboring nodes. This process is controlled by the walk depth, which determines how many nodes will be visited.
Ultipa's Random Walk algorithm implements the classical version of random walk. By default, all edges are assigned equal weights (set to 1), resulting in equal traversal probabilities. When edge weights are specified, the likelihood of traversing an edge becomes proportional to its weight. It's important to note that various variations of random walk exist, such as Node2Vec Walk and Struc2Vec Walk.
Considerations
- Self-loops can also be traversed during a random walk.
- A random walk cannot start from an isolated node, as there are no adjacent edges to follow.
- The Random Walk algorithm treats all edges as undirected, ignoring their original direction.
Example Graph
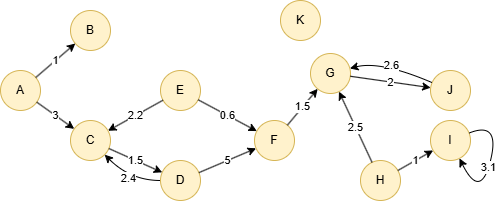
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
ALTER EDGE default ADD PROPERTY {
score float
};
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A"}),
(B:default {_id: "B"}),
(C:default {_id: "C"}),
(D:default {_id: "D"}),
(E:default {_id: "E"}),
(F:default {_id: "F"}),
(G:default {_id: "G"}),
(H:default {_id: "H"}),
(I:default {_id: "I"}),
(J:default {_id: "J"}),
(K:default {_id: "K"}),
(A)-[:default {score: 1}]->(B),
(A)-[:default {score: 3}]->(C),
(C)-[:default {score: 1.5}]->(D),
(D)-[:default {score: 2.4}]->(C),
(D)-[:default {score: 5}]->(F),
(E)-[:default {score: 2.2}]->(C),
(E)-[:default {score: 0.6}]->(F),
(F)-[:default {score: 1.5}]->(G),
(G)-[:default {score: 2}]->(J),
(H)-[:default {score: 2.5}]->(G),
(H)-[:default {score: 1}]->(I),
(I)-[:default {score: 3.1}]->(I),
(J)-[:default {score: 2.6}]->(G);
create().edge_property(@default, "score", float);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"},{_id:"B"},{_id:"C"},{_id:"D"},{_id:"E"},{_id:"F"},{_id:"G"},{_id:"H"},{_id:"I"},{_id:"J"},{_id:"K"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"B", score:1}, {_from:"A", _to:"C", score:3}, {_from:"C", _to:"D", score:1.5}, {_from:"D", _to:"C", score:2.4}, {_from:"D", _to:"F", score:5}, {_from:"E", _to:"C", score:2.2}, {_from:"E", _to:"F", score:0.6}, {_from:"F", _to:"G", score:1.5}, {_from:"G", _to:"J", score:2}, {_from:"H", _to:"G", score:2.5}, {_from:"H", _to:"I", score:1}, {_from:"I", _to:"I", score:3.1}, {_from:"J", _to:"G", score:2.6}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: random_walk
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ids |
[]_id |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies nodes to start random walk by their _id. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
uuids |
[]_uuid |
/ | / | Yes | Specifies nodes to start random walk by their _uuid. If unset, computation includes all nodes. |
walk_length |
Integer | ≥1 | 1 |
Yes | Depth of each walk, i.e., the number of nodes to visit. |
walk_num |
Integer | ≥1 | 1 |
Yes | Number of walks to perform for each specified node. |
edge_schema_property |
[]"<@schema.?><property>" |
/ | / | Yes | Numeric edge properties used as edge weights, summing values across the specified properties; edges without the specified properties are ignored. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both values to represent nodes in the results. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.random_walk.write("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
walk_length: 6,
walk_num: 2
}, {
file: {
filename: "walks"
}
})
algo(random_walk).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
return_id_uuid: "id",
walk_length: 6,
walk_num: 2
}).write({
file:{
filename: 'walks'
}})
Result:
_ids
J,G,H,G,F,D,
D,C,D,C,A,C,
F,G,H,I,I,I,
H,G,H,I,H,G,
B,A,C,E,C,D,
A,C,D,C,D,C,
E,C,E,F,E,C,
C,D,C,E,F,D,
I,I,I,H,G,J,
G,J,G,J,G,H,
J,G,J,G,F,E,
D,C,E,C,D,F,
F,D,C,A,B,A,
H,I,I,I,H,I,
B,A,B,A,C,E,
A,C,D,C,A,B,
E,F,G,F,D,F,
C,E,F,E,F,D,
I,I,H,I,I,I,
G,H,I,I,H,I,
Full Return
CALL algo.random_walk.run("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
walk_length: 6,
walk_num: 2,
edge_schema_property: 'score'
}) YIELD walks
RETURN walks
exec{
algo(random_walk).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
walk_length: 6,
walk_num: 2,
edge_schema_property: 'score'
}) as walks
return walks
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _ids |
|---|
| ["J","G","J","G","J","G"] |
| ["D","F","E","C","E","C"] |
| ["F","D","F","D","F","G"] |
| ["H","I","I","I","I","H"] |
| ["B","A","C","A","C","D"] |
| ["A","C","A","B","A","B"] |
| ["E","C","E","F","D","C"] |
| ["C","A","C","D","F","D"] |
| ["I","H","I","I","I","I"] |
| ["G","H","G","J","G","J"] |
| ["J","G","J","G","J","G"] |
| ["D","F","D","C","E","C"] |
| ["F","D","C","D","C","E"] |
| ["H","I","H","G","J","G"] |
| ["B","A","C","D","F","G"] |
| ["A","C","D","C","A","C"] |
| ["G","J","G","F","D","F"] |
| ["H","I","I","I","I","H"] |
| ["F","D","F","D","F","G"] |
| ["D","F","E","C","E","C"] |
| ["J","G","J","G","J","G"] |
Stream Return
CALL algo.random_walk.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
return_id_uuid: "id",
walk_length: 5,
walk_num: 1,
edge_schema_property: '@default.score'
}) YIELD walks
RETURN walks
exec{
algo(random_walk).params({
return_id_uuid: "id",
walk_length: 5,
walk_num: 1,
edge_schema_property: '@default.score'
}).stream() as walks
return walks
} on hdc_randomWalk
Result:
| _ids |
|---|
| ["J","G","J","G","J"] |
| ["D","F","G","J","G"] |
| ["F","G","F","D","C"] |
| ["H","G","H","G","J"] |
| ["B","A","C","D","F"] |
| ["A","C","A","C","A"] |
| ["E","F","D","F","D"] |
| ["C","D","F","D","F"] |
| ["I","I","I","I","I"] |
| ["G","H","G","J","G"] |

