Overview
The Adamic-Adar Index (AA Index) is a node similarity metric named after its creators Lada Adamic and Eytan Adar. It measures the strength of potential connection between two nodes based on their common neighbors.
- L.A. Adamic, E. Adar, Friends and Neighbors on the Web (2003)
The core idea behind the AA Index is that common neighbors with lower degrees contribute more valuable information about the similarity between two nodes than those with higher degrees. The index is calculated using the following formula:
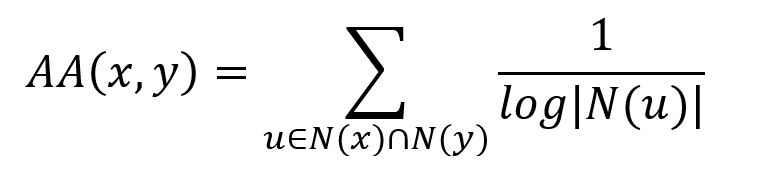
where N(u) is the set of nodes adjacent to u. For each common neighbor u of the two nodes, the AA Index first calculates the reciprocal of the logarithm of its degree |N(u)|, and then sums these values across all common neighbors.
A higher AA Index score indicates greater similarity between the nodes, while a score of 0 indicates no similarity between two nodes.
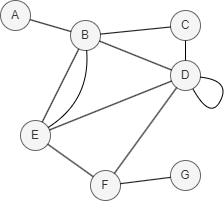
In this example, N(D) ∩ N(E) = {B, F}, where = = 1.6610, = = 2.0959, thus AA(D,E) = 1.6610 + 2.0959 = 3.7569.
Considerations
- The AA Index algorithm treats all edges as undirected, ignoring their original direction.
Example Graph
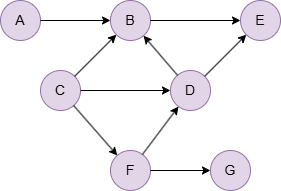
Run the following statements on an empty graph to define its structure and insert data:
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A"}),
(B:default {_id: "B"}),
(C:default {_id: "C"}),
(D:default {_id: "D"}),
(E:default {_id: "E"}),
(F:default {_id: "F"}),
(G:default {_id: "G"}),
(A)-[:default]->(B),
(B)-[:default]->(E),
(C)-[:default]->(B),
(C)-[:default]->(D),
(C)-[:default]->(F),
(D)-[:default]->(B),
(D)-[:default]->(E),
(F)-[:default]->(D),
(F)-[:default]->(G);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A"}, {_id:"B"}, {_id:"C"}, {_id:"D"}, {_id:"E"}, {_id:"F"}, {_id:"G"}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"B"}, {_from:"B", _to:"E"}, {_from:"C", _to:"B"}, {_from:"C", _to:"D"}, {_from:"C", _to:"F"}, {_from:"D", _to:"B"}, {_from:"D", _to:"E"}, {_from:"F", _to:"D"}, {_from:"F", _to:"G"}]);
Creating HDC Graph
To load the entire graph to the HDC server hdc-server-1 as my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
Parameters
Algorithm name: topological_link_prediction
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ids |
[]_id |
/ | / | No | Specifies the first group of nodes for computation by their _id. If unset, all nodes in the graph are used as the first group of nodes. |
uuids |
[]_uuid |
/ | / | No | Specifies the first group of nodes for computation by their _uuid. If unset, all nodes in the graph are used as the first group of nodes. |
ids2 |
[]_id |
/ | / | No | Specifies the second group of nodes for computation by their _id. If unset, all nodes in the graph are used as the second group of nodes. |
uuids2 |
[]_uuid |
/ | / | No | Specifies the second group of nodes for computation by their _uuid. If unset, all nodes in the graph are used as the second group of nodes. |
type |
String | Adamic_Adar |
Adamic_Adar |
Yes | Specifies the similarity type; for AA Index, keep it as Adamic_Adar. |
return_id_uuid |
String | uuid, id, both |
uuid |
Yes | Includes _uuid, _id, or both to represent nodes in the results. |
limit |
Integer | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Limits the number of results returned. Set to -1 to include all results. |
File Writeback
CALL algo.topological_link_prediction.write("my_hdc_graph", {
ids: ["C"],
ids2: ["A","E","G"],
return_id_uuid: "id"
}, {
file: {
filename: "aa"
}
})
algo(topological_link_prediction).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
ids: ["C"],
ids2: ["A","E","G"],
return_id_uuid: "id"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "aa"
}
})
Result:
_id1,_id2,result
C,A,1.66096
C,E,3.32193
C,G,2.0959
Full Return
CALL algo.topological_link_prediction.run("my_hdc_graph", {
ids: ["C"],
ids2: ["A","C","E","G"],
type: "Adamic_Adar",
return_id_uuid: "id"
}) YIELD aa
RETURN aa
exec{
algo(topological_link_prediction).params({
ids: ["C"],
ids2: ["A","C","E","G"],
type: "Adamic_Adar",
return_id_uuid: "id"
}) as aa
return aa
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id1 | _id2 | result |
|---|---|---|
| C | A | 1.660964 |
| C | E | 3.321928 |
| C | G | 2.095903 |
Stream Return
CALL algo.topological_link_prediction.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
ids: ["C"],
ids2: ["A", "B", "D", "E", "F", "G"],
type: "Adamic_Adar",
return_id_uuid: "id"
}) YIELD aa
FILTER aa.result >= 2
RETURN aa
exec{
algo(topological_link_prediction).params({
ids: ["C"],
ids2: ["A", "B", "D", "E", "F", "G"],
type: "Adamic_Adar",
return_id_uuid: "id"
}).stream() as aa
where aa.result >= 2
return aa
} on my_hdc_graph
Result:
| _id1 | _id2 | result |
|---|---|---|
| C | D | 3.756867 |
| C | E | 3.321928 |
| C | G | 2.095903 |

