UNCOLLECT releases each element of a list into an independent row and duplicates each original row and its homologous rows into a corresponding number of multiple rows. The released data stream has a length that equals the sum of lengths of all the lists that have been released from the original data stream.
Syntax: UNCOLLECT <expression1> as <alias1>, <expression2> as <alias2>, ...
Input
- <expression>: The list to be released
- <alias>: The alias acquired after the list is released, mandatory
When releasing multiple data streams of lists, the released length of lists in each row is subject to the list in that row with the most number of elements, filling with
nullif insufficient.
For instance, release all the nodes in path, homologous alias path and a1 have 2 rows, after release path and a2 have 6 rows:
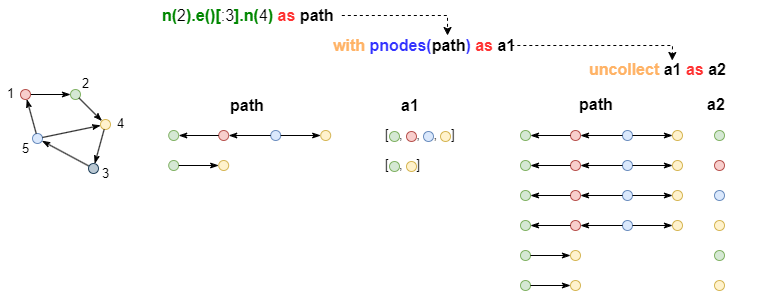
n(2).e()[:3].n(4) as path
with pnodes(path) as a1
uncollect a1 as a2
return path, a2
Another instance is given for releasing two data streams s1 and s2, where the [1,2] in the first row of s2 and the ["d","e"] in the second row of s1 are supplemented with null in order to fill up the length:
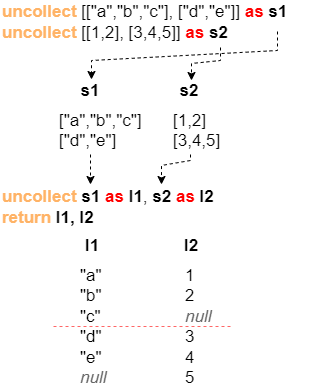
uncollect [["a","b","c"],["d","e"]] as s1
uncollect [[1,2],[3,4,5]] as s2
uncollect s1 as l1, s2 as l2
return l1, l2
Sample graph: (to be used for the following examples)
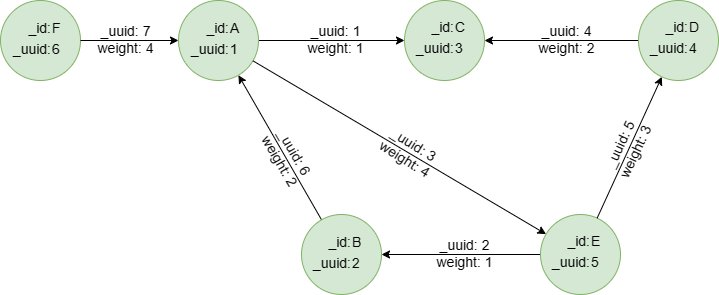
create().edge_property(@default, "weight", int32)
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A", _uuid:1}, {_id:"B", _uuid:2}, {_id:"C", _uuid:3}, {_id:"D", _uuid:4}, {_id:"E", _uuid:5}, {_id:"F", _uuid:6}])
insert().into(@default).edges([{_uuid:1, _from_uuid:1, _to_uuid:3, weight:1}, {_uuid:2, _from_uuid:5, _to_uuid:2 , weight:1}, {_uuid:3, _from_uuid:1, _to_uuid:5 , weight:4}, {_uuid:4, _from_uuid:4, _to_uuid:3 , weight:2}, {_uuid:5, _from_uuid:5, _to_uuid:4 , weight:3}, {_uuid:6, _from_uuid:2, _to_uuid:1 , weight:2}, {_uuid:7, _from_uuid:6, _to_uuid:1 , weight:4}])
Common Usage
Example: Find 2-step paths from A to D, deduplicate all the involved nodes and return
n({_id == "A"}).e()[2].n({_id == "D"}) as p
uncollect pnodes(p) as a
with dedup(a) as b
return b{*}
| _id | _uuid |
|-----|-------|
| A | 1 |
| C | 3 |
| D | 4 |
| E | 5 |

