The spread().src().depth() query can find and return edges from a start node within K hops, by specifying k-index, applying filters on the initial-node, all edges and all neighbor nodes. The found edges are returned from shallower to deeper, in form of 1-step paths (start node, edge, end node).
Spread is a BFS (Breadth First Search) query method that is commonly used in graph query/analysis industry for observing layers of relationship around an entity, and to retrieve and acquire data quickly.
Syntax:
- Statement alias: supported (PATH)
- All parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Specification | Description | Structure of Custom Alias |
|---|---|---|---|---|
src() |
Filter | Mandatory | The filtering rules of the start node; error will occur if multiple nodes are found | NODE |
depth() |
Int | >0; mandatory | The maximum depth to spread | Not supported |
node_filter() |
Filter | The filtering rules that neighbor nodes other than src need to satisfy |
Not supported | |
edge_filter() |
Filter | The filtering rules that all edges need to satisfy | Not supported | |
direction() |
String | left, right | To specify the direction of the edge | Not supported |
limit() |
Int | -1 or >=0 | Number of results to return for each subquery, -1 means to return all results | Not supported |
Sample graph: (to be used for the following examples)
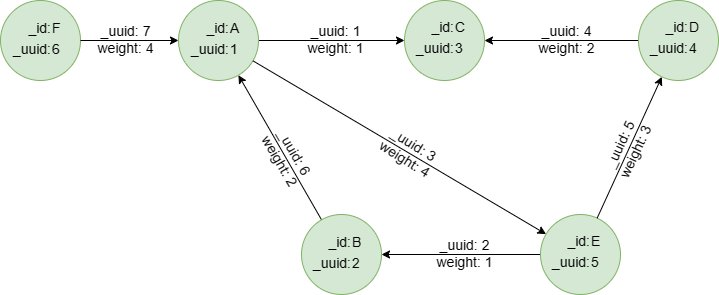
create().edge_property(@default, "weight", int32)
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A", _uuid:1}, {_id:"B", _uuid:2}, {_id:"C", _uuid:3}, {_id:"D", _uuid:4}, {_id:"E", _uuid:5}, {_id:"F", _uuid:6}])
insert().into(@default).edges([{_uuid:1, _from_uuid:1, _to_uuid:3, weight:1}, {_uuid:2, _from_uuid:5, _to_uuid:2 , weight:1}, {_uuid:3, _from_uuid:1, _to_uuid:5 , weight:4}, {_uuid:4, _from_uuid:4, _to_uuid:3 , weight:2}, {_uuid:5, _from_uuid:5, _to_uuid:4 , weight:3}, {_uuid:6, _from_uuid:2, _to_uuid:1 , weight:2}, {_uuid:7, _from_uuid:6, _to_uuid:1 , weight:4}])
Filter Depth
Find 1~2-Hop edges of node D, return as paths and carry all properties
spread().src({_id == "D"}).depth(2) as e
return e{*}
A --1--> C
E --5--> D
A --3--> E
D --4--> C
E --2--> B
B --6--> A
Analysis: Both the start node and end node of edge 6 are from 2-Hop of node D, edge 6 is also considered as from 2-Hop of node D.
Filter Neighbor Nodes
Example: Find 1~2-Hop edges of node D, whose shortest path does not pass node E, return as paths and carry all properties
spread().src({_id == "D"}).depth(2)
.node_filter({_id != "E"}) as e
return e{*}
A --1--> C
D --4--> C
Analysis: When the shortest path are not allowed to pass node E, it is equivalent to removing node E and its adjacent edges 2, 3 and 5 from the graph, in which case edge 6 is from 3-Hop of node D and not presents in the result.
Filter Edges
Example: Find 1~2-Hop edges of node D, whose shortest path does not pass edge 5, return as paths and carry all properties
spread().src({_id == "D"}).depth(2)
.edge_filter({_uuid != 5}) as e
return e{*}
A --1--> C
D --4--> C
Analysis: When the shortest path are not allowed to pass edge 5, it is equivalent to removing edge 5 from the graph, in which case edge 3 and 6 are from 3-Hop of node D, edge 2 is from 4-Hop of node D.
Filter Edge Direction
Example: Find 1~2-Hop edges of node D, with all edges right-pointing, return as paths and carry all properties
spread().src({_id == "D"}).depth(2)
.direction(right) as e
return e{*}
D --4--> C
When all edges in the shortest path are right-pointing (outbound), node D has only one 1-Hop edge 4, and has no edge from 2-Hop or deeper since the end node of edge 4 has no outbound edge.
Example: Find 1~2-Hop edges of node D, with all edges left-pointing, return as paths and carry all properties
spread().src({_id == "D"}).depth(2)
.direction(left) as e
return e{*}
E --5--> D
A --3--> E
Analysis: When all edges in the shortest path are left-pointing (inbound), node D has a 1-Hop edge 5 and a 2-Hop edge 3.
Limit Result of Sub-Query
Example: Find three 1~3-Hop edges of node D, return as paths and carry all properties
spread().src({_id == "D"}).depth(3).limit(3) as e
return e{*}
E --5--> D
A --3--> E
D --4--> C

