Overview
Graph centrality of a node is measured by the maximum shortest distance from the node to all other reachable nodes. This measurement, along with other measurements like closeness centrality and graph diameter, can be considered jointly to determine whether a node is literally located at the very center of the graph.
Graph centrality takes on values between 0 to 1, nodes with higher scores are closer to the center.
Concepts
Shortest Distance
The shortest distance of two nodes is the number of edges contained in the shortest path between them. Please refer to Closeness Centrality for more details.
Graph Centrality
Graph centrality score of a node defined by this algorithm is the inverse of the maximum shortest distance from the node to all other reachable nodes. The formula is:
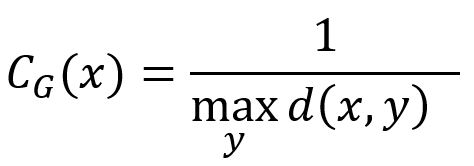
where x is the target node, y is any node that connects with x along edges (x itself is excluded), d(x,y) is the shortest distance between x and y.
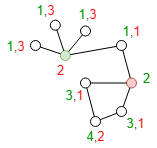
In this graph, the green number and red number next to each node is the shortest distance between the node and the green node and red node. Graph centrality scores of the green and red nodes are 1/4 = 0.25 and 1/3 = 0.3333 respectively.
Regarding closeness centrality, the green node has score 8/(1+1+1+1+2+3+4+3) = 0.5, the red node has score 8/(3+3+3+2+1+1+2+1) = 0.5. When two nodes have the same closeness centrality score, graph centrality can be viewed as the subsidiary basis to determine which node is closer to the center.
Graph Centrality algorithm consumes considerable computing resources. For a graph with V nodes, it is recommended to perform (uniform) sampling when V > 10,000, and the suggested number of samples is the base-10 logarithm of the number of nodes (
log(V)).
For each execution of the algorithm, sampling is performed only once, centrality score of each node is computed based on the shortest distance between the node and all sample nodes.
Considerations
- The graph centrality score of isolated nodes is 0.
- The Graph Centrality algorithm ignores the direction of edges but calculates them as undirected edges.
Syntax
- Command:
algo(graph_centrality) - Parameters:
Name |
Type |
Spec |
Default |
Optional |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ids / uuids | []_id / []_uuid |
/ | / | Yes | ID/UUID of the nodes to calculate, calculate for all nodes if not set |
| direction | string | in, out |
/ | Yes | Direction of all edges in the shortest path, in for incoming direction, out for outgoing direction |
| sample_size | int | -1, -2, [1, V] |
-2 |
Yes | Number of samples to compute centrality scores; -1 means to sample log(V) nodes; -2 means not to perform sampling; a number within [1, V] means to sample the set number of nodes; sample_size is only valid when ids (uuids) is ignored or when it specifies all nodes |
| limit | int | ≥-1 | -1 |
Yes | Number of results to return, -1 to return all results |
| order | string | asc, desc |
/ | Yes | Sort nodes by the centrality score |
Examples
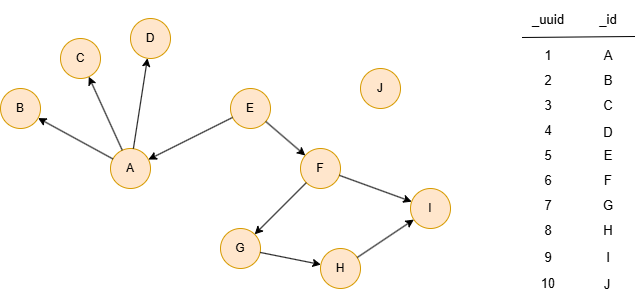
The example graph is as follows:
File Writeback
| Spec | Content |
|---|---|
| filename | _id,centrality |
algo(graph_centrality).params().write({
file:{
filename: 'res'
}
})
Results: File res
J,0
I,0.25
H,0.2
F,0.333333
G,0.25
D,0.2
E,0.333333
C,0.2
A,0.25
B,0.2
Property Writeback
| Spec | Content | Write to | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| property | centrality |
Node property | float |
algo(graph_centrality).params().write({
db:{
property: 'gc'
}
})
Results: Centrality score for each node is written to a new property named gc
Direct Return
Alias Ordinal |
Type |
Description | Columns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | []perNode | Node and its centrality | _uuid, centrality |
algo(graph_centrality).params({
ids: ['A', 'B', 'C'],
order: 'asc'
}) as gc
return gc
Results: gc
| _uuid | centrality |
|---|---|
| 2 | 0.2 |
| 3 | 0.2 |
| 1 | 0.25 |
Stream Return
Alias Ordinal |
Type |
Description | Columns |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | []perNode | Node and its centrality | _uuid, centrality |
algo(graph_centrality).params().stream() as gc
where gc.centrality > 0.25
return gc
Results: gc
| _uuid | centrality |
|---|---|
| 6 | 0.333333 |
| 5 | 0.333333 |

