Function coalesce() returns the left-most non null value from multiple (≥2) values, or returns null if all values are null.
When multiple values are of different data structures, data conversion might be triggered to guarantee a consistent data type in the final data stream.
Occasions when
nullvalue is produced: properties not provided when inserting data, properties created after data is inserted, calling a property that is not existent.
Arguments:
- Any value <any>
- ...
Returns:
- Result <any>
Sample graph: (to be used for the following examples)
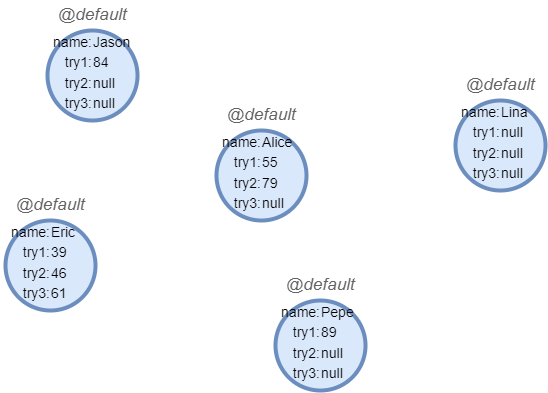
create().node_property(@default, "name").node_property(@default, "try1", int32).node_property(@default, "try2", int32).node_property(@default, "try3", int32)
insert().into(@default).nodes([{name:"Jason", try1:84}, {name:"Alice", try1:55, try2:79}, {name:"Lina"}, {name:"Eric", try1:39, try2:46, try3:61}, {name:"Pepe", try1:89}])
Common Usage
Example: Return the score of the last test that each student takes, knowing that each student has three chances, and retesting is allowed only if the previous one failed. Return -1 if a student does not give any try.
find().nodes() as n
return table(n.name, coalesce(n.try3, n.try2, n.try1, -1))
| n.name | coalesce(n.try3, n.try2, n.try1, -1) |
|--------|--------------------------------------|
| Jason | 84 |
| Alice | 79 |
| Lina | -1 |
| Eric | 61 |
| Pepe | 89 |

